MicroRNA-551b-3p inhibits tumour growth of human cholangiocarcinoma by targeting Cyclin D1
- PMID: 31199052
- PMCID: PMC6653057
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14312
MicroRNA-551b-3p inhibits tumour growth of human cholangiocarcinoma by targeting Cyclin D1
Abstract
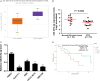
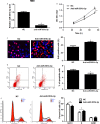
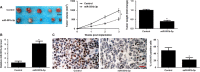
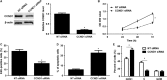
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are powerful regulators in the tumorigenesis of cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). Previous studies report that miR-551b-3p acts as an oncogenic factor in ovarian cancer, but plays a tumour suppressive role in gastric cancer. However, the expression pattern and potential function of miR-551b-3p were still unclear in CCA. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the expression of miR-551b-3p and its role as well as molecular mechanism in CCA. Analysis of TCGA dataset suggested that miR-551b-3p was under-expressed in CCA tissues compared to normal bile duct tissues. Furthermore, our data confirmed the decreased levels of miR-551b-3p in CCA samples and cell lines. Interestingly, TCGA data suggested that low miR-551b-3p level indicated reduced overall survival of CCA patients. Gain- and loss-of-function experiments found that miR-551b-3p inhibited the proliferation, G1-S phase transition and induced apoptosis of CCA cells. In vivo experiments revealed that ectopic expression of miR-551b-3p inhibited tumour growth of CCA in mice. Further investigation demonstrated that miR-551b-3p directly bond to the 3'-UTR of Cyclin D1 (CCND1) mRNA and negatively regulated the abundance of CCND1 in CCA cells. An inverse correlation between miR-551b-3p expression and the level of CCND1 mRNA was detected in CCA tissues from TCGA dataset. Notably, CCND1 knockdown showed similar effects to miR-551b-3p overexpression in HuCCT-1 cells. CCND1 restoration rescued miR-551b-3p-induced inhibition of proliferation, G1 phase arrest and apoptosis in HuCCT-1 cells. In summary, miR-551b-3p inhibits the expression of CCND1 to suppress CCA cell proliferation and induce apoptosis, which may provide a theoretical basis for improving CCA treatment.
Keywords: Cyclin D1; cholangiocarcinoma; microRNA-551b-3p; tumour growth.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Banales JM, Cardinale V, Carpino G, et al. Expert consensus document: cholangiocarcinoma: current knowledge and future perspectives consensus statement from the European Network for the Study of Cholangiocarcinoma (ENS‐CCA). Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13:261‐280. - PubMed
-
- Doherty B, Nambudiri VE, Palmer WC. Update on the diagnosis and treatment of cholangiocarcinoma. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2017;19:2. - PubMed
-
- Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857‐866. - PubMed
-
- Xu Q, Zhu Q, Zhou Z, et al. MicroRNA‐876‐5p inhibits epithelial‐mesenchymal transition and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting BCL6 corepressor like 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;103:645‐652. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

