Factors Determining Patients' Choice Between Mobile Health and Telemedicine: Predictive Analytics Assessment
- PMID: 31199332
- PMCID: PMC6592402
- DOI: 10.2196/13772
Factors Determining Patients' Choice Between Mobile Health and Telemedicine: Predictive Analytics Assessment
Abstract
Background: The solution to the growing problem of rural residents lacking health care access may be found in the use of telemedicine and mobile health (mHealth). Using mHealth or telemedicine allows patients from rural or remote areas to have better access to health care.
Objective: The objective of this study was to understand factors influencing the choice of communication medium for receiving care, through the analysis of mHealth versus telemedicine encounters with a virtual urgent clinic.
Methods: We conducted a postdeployment evaluation of a new virtual health care service, Virtual Urgent Clinic, which uses mHealth and telemedicine modalities to provide patient care. We used a multinomial logistic model to test the significance and predictive power of a set of features in determining patients' preferred method of telecare encounters-a nominal outcome variable of two levels (mHealth and telemedicine).
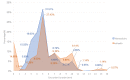
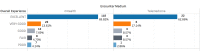
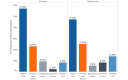
Results: Postdeployment, 1403 encounters were recorded, of which 1228 (87.53%) were completed with mHealth and 175 (12.47%) were telemedicine encounters. Patients' sex (P=.004) and setting (P<.001) were the most predictive determinants of their preferred method of telecare delivery, with significantly small P values of less than .01. Pearson chi-square test returned a strong indication of dependency between chief concern and encounter mediums, with an extremely small P<.001. Of the 169 mHealth patients who responded to the survey, 154 (91.1%) were satisfied by their encounter, compared with 31 of 35 (89%) telemedicine patients.
Conclusions: We studied factors influencing patients' choice of communication medium, either mHealth or telemedicine, for a virtual care clinic. Sex and geographic location, as well as their chief concern, were strong predictors of patients' choice of communication medium for their urgent care needs. This study suggests providing the option of mHealth or telemedicine to patients, and suggesting which medium would be a better fit for the patient based on their characteristics.
Keywords: mHealth; predictive analytics; telemedicine; urgent care.
©Saif Khairat, Songzi Liu, Tanzila Zaman, Barbara Edson, Robert Gianforcaro. Originally published in JMIR Mhealth and Uhealth (http://mhealth.jmir.org), 08.06.2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Wilson NW, Couper ID, De Vries E, Reid S, Fish T, Marais BJ. A critical review of interventions to redress the inequitable distribution of healthcare professionals to rural and remote areas. Rural Remote Health. 2009;9(2):1060. http://www.rrh.org.au/articles/subviewnew.asp?ArticleID=1060 1060 - PubMed
-
- America Counts Staff One in five Americans live in rural areas. 2017. Aug 9, [2019-05-23]. https://www.census.gov/library/stories/2017/08/rural-america.html .
-
- Laditka JN, Laditka SB, Probst JC. Health care access in rural areas: evidence that hospitalization for ambulatory care-sensitive conditions in the United States may increase with the level of rurality. Health Place. 2009 Sep;15(3):731–40. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2008.12.007.S1353-8292(09)00005-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anderson TJ, Saman DM, Lipsky MS, Lutfiyya MN. A cross-sectional study on health differences between rural and non-rural U.S. counties using the County Health Rankings. BMC Health Serv Res. 2015 Oct 01;15:441. doi: 10.1186/s12913-015-1053-3. https://bmchealthservres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12913-015-1... 10.1186/s12913-015-1053-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical