Evaluation of EGFR inhibitor-mediated acneiform skin toxicity within the double-blind randomized EVITA trial: A thorough gender-specific analysis using the WoMo score
- PMID: 31199595
- PMCID: PMC6675717
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2132
Evaluation of EGFR inhibitor-mediated acneiform skin toxicity within the double-blind randomized EVITA trial: A thorough gender-specific analysis using the WoMo score
Abstract
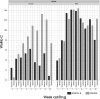
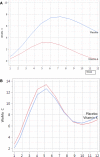
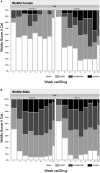
Acne-like skin reactions frequently occur in patients undergoing treatment with drugs inhibiting the epidermal growth factor receptor. Recently, the effects of vitamin K1 containing cream (Reconval K1) as prophylactic skin treatment in addition to doxycycline were explored in a double-blind randomized phase II trial (EVITA) in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer receiving cetuximab. EVITA demonstrated a trend towards less severe skin rash in Reconval K1-treated patients using the tripartite WoMo skin reaction grading score as a thorough tool for quantification of drug related skin reactions. This gender-specific analysis of the EVITA trial evaluated the application of the WoMo score for assessment of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-related skin toxicities according to treatment arm and gender. To show the robustness of results parametric and non-parametric statistical analyses were conducted. All three parts of the WoMo score independently demonstrated the superiority of the treatment arm (Reconval K1) regarding a significant reduction in acneiform skin reactions in women. Men did not benefit from Reconval K1 cream at any time point in none of the WoMo score analyses. The treatment effect in women was confirmed by the use of skin rash categories based on the final WoMo overall score and mixed effect longitudinal multiple linear regression analysis. The WoMo score represents a sensitive tool for studies exploiting treatments against EGFR mediated acne-like skin rash. Part C of the WoMo score seems to be sufficient for quantification of drug related skin toxicities in further studies. Standard WoMo skin reaction score values for future studies are provided.
Keywords: EGFR inhibitor; WoMo score; acneiform skin toxicity; women.
© 2019 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
MRG has received honoraria from Roche, MSD, BMS, Merck KGaA, Novartis, Pierre Fabre. S‐E A‐B has an advisory role with Merck, Roche, Celgene, Lilly, Nordic Pharma, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, and MSD Sharp & Dohme; is a speaker for Roche, Celgene, Lilly, Nordic Pharma, AIO gGmbH, MCI, promedicis, and Forum für Medizinische Fortbildung; He is CEO/founder of IKF Klinische Krebsforschung GmbH and has received research grants from Sanofi, Merck, Roche, Celgene, Vifor, Medac, Hospira, Lilly, German Cancer Aid (Krebshilfe), German Research Foundation and the Federal Ministry of Education and Research. RDH has received honoraria from Merck KGaA, Amgen, Roche, MSD, BMS, medac, Lilly, Sanofi, Boehringer. He has served as an advisor for Amgen, Merck KGaA, Roche, MSD, BMS, medac, Lilly, Sanofi, Boehringer. His institution has received research funding from Amgen, Merck KGaA, Amgen, Sanofi. All remaining authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hofheinz RD, Segaert S, Safont MJ, Demonty G, Prenen H. Management of adverse events during treatment of gastrointestinal cancers with epidermal growth factor inhibitors. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017;114:102‐113. - PubMed
-
- Lacouture ME, Mitchell EP, Piperdi B, et al. Skin toxicity evaluation protocol with panitumumab (STEPP), a phase II, open‐label, randomized trial evaluating the impact of a pre‐Emptive Skin treatment regimen on skin toxicities and quality of life in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1351‐1357. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi Y, Komatsu Y, Yuki S, et al. Randomized controlled trial on the skin toxicity of panitumumab in Japanese patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: HGCSG1001 study. J‐STEPP. Future Oncol. 2015;11:617‐627. - PubMed
-
- Hofheinz RD, Lorenzen S, Trojan J, et al. EVITA – A double‐blind, vehicle controlled, randomized phase II trial of vitamin K1 cream as prophylaxis for cetuximab‐induced skin toxicity. Ann Oncol. 2018;29:1010‐1015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

