Immunoglobulin G structure and rheumatoid factor epitopes
- PMID: 31199818
- PMCID: PMC6568389
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217624
Immunoglobulin G structure and rheumatoid factor epitopes
Abstract
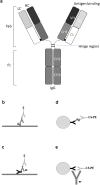
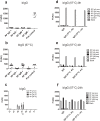
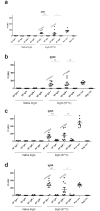
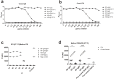
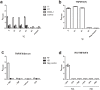
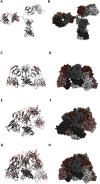
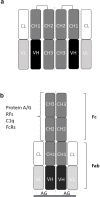
Antibodies are important for immunity and exist in several classes (IgM, IgD, IgA, IgG, IgE). They are composed of symmetric dimeric molecules with two antigen binding regions (Fab) and a constant part (Fc), usually depicted as Y-shaped molecules. Rheumatoid factors found in patients with rheumatoid arthritis are autoantibodies binding to IgG and paradoxically appear to circulate in blood alongside with their antigen (IgG) without reacting with it. Here, it is shown that rheumatoid factors do not react with native IgG in solution, and that their epitopes only become accessible upon certain physico-chemical treatments (e.g. heat treatment at 57 °C), by physical adsorption on a hydrophobic surface or by antigen binding. Moreover, chemical cross-linking in combination with mass spectrometry showed that the native state of IgG is a compact (closed) form and that the Fab parts of IgG shield the Fc region and thereby control access of rheumatoid factors and presumably also some effector functions. It can be inferred that antibody binding to pathogen surfaces induces a conformational change, which exposes the Fc part with its effector sites and rheumatoid factor epitopes. This has strong implications for understanding antibody structure and physiology and necessitates a conceptual reformulation of IgG models.
Conflict of interest statement
Statens Serum Institut has filed a patent application (EP 18169502.4) on the use of heat-treated immunoglobulins in immunoassays with GH as inventor. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
References
-
- Murphy K. Immunobiology. Garland Science, NY, USA; 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

