Cordycepin kills Mycobacterium tuberculosis through hijacking the bacterial adenosine kinase
- PMID: 31199855
- PMCID: PMC6568415
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218449
Cordycepin kills Mycobacterium tuberculosis through hijacking the bacterial adenosine kinase
Abstract
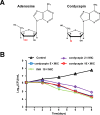
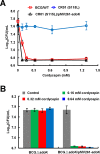
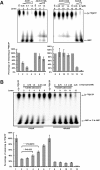
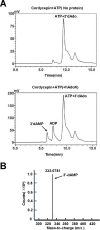
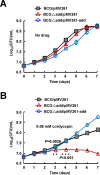
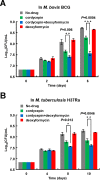
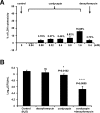
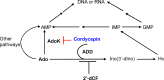
Cordycepin is an efficient component of Cordyceps spp, a traditional Chinese medicine widely used for healthcare in China, and has been recently acted as a strong anticancer agent for clinic. However, whether and how it may play a role in combating tuberculosis, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, remains unknown. Here we report that cordycepin can kill Mycobacterium by hijacking the bacterial adenosine kinase (AdoK), a purine salvage enzyme responsible for the phosphorylation of adenosine (Ado) to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). We show that cordycepin is a poor AdoK substrate but it competitively inhibits the catalytic activity of AdoK for adenosine phosphorylation. Cordycepin does not affect the activity of the human adenosine kinase (hAdoK), whereas hAdoK phosphorylates cordycepin to produce a new monophosphate derivative. Co-use of cordycepin and deoxycoformycin, an inhibitor of adenosine deaminase (ADD), more efficiently kills M. bovis and M. tuberculosis. The add-deleted mycobacterium is more sensitive to cordycepin. This study characterized cordycepin as a new mycobactericidal compound and also uncovered a potential anti-mycobacterial mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2018. WHO; 2017.
-
- Cunningham KG, Manson W, Spring FS, Hutchinson SA. Cordycepin, a metabolic product isolated from cultures of Cordyceps militaris (Linn.) Link. Nature 1950;166:949. - PubMed
-
- Zhou XX, Meyer CU, Schmidtke P, Zepp F. Effect of cordycepin on interleukin-10 production of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Eur J Pharmacol 2002;453:309–317. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura K, Yoshikawa N, Yamaguchi Y, Kagota S, Shinozuka K, Kunitomo M. Antitumor effect of cordycepin (3’-deoxyadenosine) on mouse melanoma and lung carcinoma cells involves adenosine A3 receptor stimulation. Anticancer Res 2006;26:43–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

