Ouabain-regulated phosphoproteome reveals molecular mechanisms for Na+, K+-ATPase control of cell adhesion, proliferation, and survival
- PMID: 31199885
- PMCID: PMC6704450
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201900445R
Ouabain-regulated phosphoproteome reveals molecular mechanisms for Na+, K+-ATPase control of cell adhesion, proliferation, and survival
Abstract
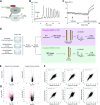
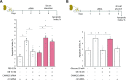
The ion pump Na+, K+-ATPase (NKA) is a receptor for the cardiotonic steroid ouabain. Subsaturating concentration of ouabain triggers intracellular calcium oscillations, stimulates cell proliferation and adhesion, and protects from apoptosis. However, it is controversial whether ouabain-bound NKA is considered a signal transducer. To address this question, we performed a global analysis of protein phosphorylation in COS-7 cells, identifying 2580 regulated phosphorylation events on 1242 proteins upon 10- and 20-min treatment with ouabain. Regulated phosphorylated proteins include the inositol triphosphate receptor and stromal interaction molecule, which are essential for initiating calcium oscillations. Hierarchical clustering revealed that ouabain triggers a structured phosphorylation response that occurs in a well-defined, time-dependent manner and affects specific cellular processes, including cell proliferation and cell-cell junctions. We additionally identify regulation of the phosphorylation of several calcium and calmodulin-dependent protein kinases (CAMKs), including 2 sites of CAMK type II-γ (CAMK2G), a protein known to regulate apoptosis. To verify the significance of this result, CAMK2G was knocked down in primary kidney cells. CAMK2G knockdown impaired ouabain-dependent protection from apoptosis upon treatment with high glucose or serum deprivation. In conclusion, we establish NKA as the coordinator of a broad, tightly regulated phosphorylation response in cells and define CAMK2G as a downstream effector of NKA.-Panizza, E., Zhang, L., Fontana, J. M., Hamada, K., Svensson, D., Akkuratov, E. E., Scott, L., Mikoshiba, K., Brismar, H., Lehtiö, J., Aperia, A. Ouabain-regulated phosphoproteome reveals molecular mechanisms for Na+, K+-ATPase control of cell adhesion, proliferation, and survival.
Keywords: apoptosis; calcium and calmodulin–dependent protein kinase; inositol triphosphate receptor; kidney; phosphoproteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by the Swedish Research Council (VR), the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research (SSF), the Swedish Cancer Society (Cancerfonden), the Erling-Persson Family Foundation, the Märta and Gunnar V. Philipsons Foundation, the Swedish Childhood Cancer Society (Barncancerfonden), and the Karolinska Institutet Doctoral (KID) funding. D.S. is supported by a Novo Nordisk postdoctoral fellowship run in partnership with the Karolinska Institutet. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kaplan J. H. (2002) Biochemistry of Na,K-ATPase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71, 511–535 - PubMed
-
- Schoner W., Scheiner-Bobis G. (2005) Endogenous cardiac glycosides: hormones using the sodium pump as signal transducer. Semin. Nephrol. 25, 343–351 - PubMed
-
- Murata Y., Matsuda T., Tamada K., Hosoi R., Asano S., Takuma K., Tanaka K., Baba A. (1996) Ouabain-induced cell proliferation in cultured rat astrocytes. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 72, 347–353 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

