Effectiveness and Estimation of Cost-Effectiveness of a Group-Based Multicomponent Physical Exercise Programme on Risk of Falling and Frailty in Community-Dwelling Older Adults
- PMID: 31200434
- PMCID: PMC6617042
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16122086
Effectiveness and Estimation of Cost-Effectiveness of a Group-Based Multicomponent Physical Exercise Programme on Risk of Falling and Frailty in Community-Dwelling Older Adults
Abstract
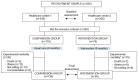
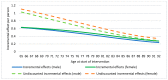
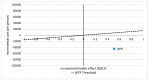
This study analyses the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of a group-based multicomponent physical exercise programme aimed at reducing the risk of falling and frailty in community-dwelling older adults. This is a pretest-posttest non-equivalent control group design, with an intervention group and a comparison group. Participants were evaluated at baseline and after 9 months. The effectiveness analyses showed significant reduction in the risk of falling (-45.5%; p = 0.000) and frailty (-31%; p = 0.000) after the intervention for the participants in the physical exercise programme. Moreover, these participants showed an improvement in limitations in activities of daily living, self-care ability and the use of health resources, physical performance, balance and body mass index. The cost-effectiveness analyses showed that the intervention was cost-saving and more effective than usual care scenario. A novel group-based multicomponent physical exercise programme showed to be more effective and cost-effective than usual care for older adults suffering from risk of falling and frailty.
Keywords: ageing; falls; frailty; older adults; physical exercise; risk of falling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- European Commission . European Commission; 2016. [(accessed on 2 May 2018)]. Injury Database. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/health/data_collection/databases/idb/index_en.htm.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

