Deregulation of miRNA in Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastric MALT Lymphoma: From Mice to Human
- PMID: 31200531
- PMCID: PMC6616415
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8060845
Deregulation of miRNA in Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastric MALT Lymphoma: From Mice to Human
Abstract
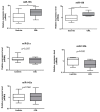
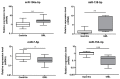
Gastric MALT lymphoma (GML) is directly caused by Helicobacter pylori infection but occurs only in a small number of infected subjects. Mechanisms underlying the initiation and progression of GML remain unclear. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that are now considered as major players in inflammation and carcinogenesis, acting as oncogenes or tumor suppressors. Previous laboratory studies have shown in a GML mouse model that overexpression of a distinct set of five miRNAs (miR-21a, miR-135b, miR-142a, miR-150, miR-155) could play a critical role in the pathogenesis of GML. Our goal was to compare the miRNA expression profile obtained in the GML mouse model to that in human GML (11 cases of GML compared to 17 cases of gastritis control population). RTqPCR on the five dysregulated miRNAs in the GML mouse model and PCR array followed by RTqPCR confirmation showed that four miRNAs were up-regulated (miR-150, miR-155, miR-196a, miR-138) and two miRNAs down-regulated (miR-153, miR-7) in the stomachs of GML patients vs. gastritis control population. The analysis of their validated targets allowed us to postulate that these miRNAs (except miR-138) could act synergistically in a common signaling cascade promoting lymphomagenesis and could be involved in the pathogenesis of GML.
Keywords: Helicobacter; MALT lymphoma; miRNA; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zucca E., Copie-Bergman C., Ricardi U., Thieblemont C., Raderer M., Ladetto M., on behalf of the ESMO Guidelines Working Group Gastric marginal zone lymphoma of MALT type: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2013;24:vi144–vi148. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt343. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fischbach W., Goebeler-Kolve M.-E., Dragosics B., Greiner A., Stolte M. Long term outcome of patients with gastric marginal zone B cell lymphoma of mucosa associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) following exclusive Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy: Experience from a large prospective series. Gut. 2004;53:34–37. doi: 10.1136/gut.53.1.34. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

