In Depth Quantification of Extracellular Matrix Proteins from Human Pancreas
- PMID: 31200599
- PMCID: PMC7024561
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00241
In Depth Quantification of Extracellular Matrix Proteins from Human Pancreas
Abstract
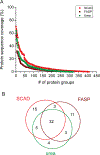
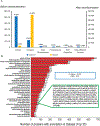
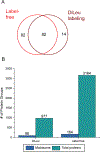
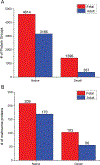
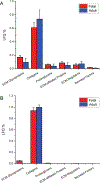
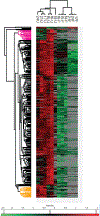
Extracellular matrix (ECM) is an important component of the pancreatic microenvironment which regulates β cell proliferation, differentiation, and insulin secretion. Protocols have recently been developed for the decellularization of the human pancreas to generate functional scaffolds and hydrogels. In this work, we characterized human pancreatic ECM composition before and after decellularization using isobaric dimethylated leucine (DiLeu) labeling for relative quantification of ECM proteins. A novel correction factor was employed in the study to eliminate the bias introduced during sample preparation. In comparison to the commonly employed sample preparation methods (urea and FASP) for proteomic analysis, a recently developed surfactant and chaotropic agent assisted sequential extraction/on pellet digestion (SCAD) protocol has provided an improved strategy for ECM protein extraction of human pancreatic ECM matrix. The quantitative proteomic results revealed the preservation of matrisome proteins while most of the cellular proteins were removed. This method was compared with a well-established label-free quantification (LFQ) approach which rendered similar expressions of different categories of proteins (collagens, ECM glycoproteins, proteoglycans, etc.). The distinct expression of ECM proteins was quantified comparing adult and fetal pancreas ECM, shedding light on the correlation between matrix composition and postnatal β cell maturation. Despite the distinct profiles of different subcategories in the native pancreas, the distribution of matrisome proteins exhibited similar trends after the decellularization process. Our method generated a large data set of matrisome proteins from a single tissue type. These results provide valuable insight into the possibilities of constructing a bioengineered pancreas. It may also facilitate better understanding of the potential roles that matrisome proteins play in postnatal β cell maturation.
Keywords: FASP; SCAD; decellularized pancreas; dimethylated leucine (DiLeu); extracellular matrix (ECM); isobaric quantitation; label-free quantitation (LFQ); matrisome; urea.
Conflict of interest statement
Notes
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): JSO is scientific co-founder and Chief Scientific Officer, of Regenerative Medical Solutions, Inc. and has stock equity.
Figures
References
-
- Beattie GM; Rubin JS; Mally MI; Otonkoski T; Hayek A Regulation of Proliferation and Differentiation of Human Fetal Pancreatic Islet Cells by Extracellular Matrix, Hepatocyte Growth Factorand Cell-Cell Contact. Diabetes 1996, 45, 1223–1228. - PubMed
-
- Jiang FX; Cram DS; DeAizpurua HJ; Harrison LC Laminin-1 Promotes Differentiation of Fetal Mouse Pancreatic Beta-Cells. Diabetes 1999, 48 (4), 722–730. - PubMed
-
- Edamura K; Nasu K; Iwami Y; Ogawa H; Sasaki N; Ohgawara H Effect of Adhesion or Collagen Molecules on Cell Attachment, Insulin Secretion, and Glucose Responsiveness in the Cultured Adult Porcine Endocrine Pancreas: A Preliminary Study. Cell Transplant 2003, 12 (4), 439–446. - PubMed
-
- Ryschich E; Khamidjanov A; Kerkadze V; Büchler MW; Zöller M; Schmidt J Promotion of Tumor Cell Migration by Extracellular Matrix Proteins in Human Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas 2009, 38 (7), 804–810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

