Medium-term health-related quality of life in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension treated with goal-oriented sequential combination therapy based on exercise capacity
- PMID: 31200710
- PMCID: PMC6570916
- DOI: 10.1186/s12955-019-1178-x
Medium-term health-related quality of life in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension treated with goal-oriented sequential combination therapy based on exercise capacity
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) remains a life-threatening condition, despite modern therapies. We prospectively investigated the therapeutic health-related quality of life (HRQOL) effects of goal-oriented sequential combination therapy based on exercise capacity in patients newly diagnosed with PAH.
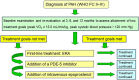
Methods: To examine the changes in HRQOL in PAH patients, we treated 30 patients newly diagnosed with PAH with goal-oriented sequential combination therapy based on exercise capacity. We monitored exercise capacity by cardiopulmonary exercise testing and observed the benefit of using a peak VO2 cut-off of 15 mL/kg/min to guide combination therapy. First-line treatment was an endothelin receptor antagonist (ERA); second-line treatment was the addition of a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE-5I). At baseline and at 3, 6, and 12 months, HRQOL was evaluated by using the eight-item Medical Outcomes Survey Short Form Health Survey.
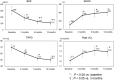
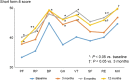
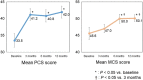
Results: At 12 months, 100% of PAH patients were receiving an ERA, and 82% an ERA + PDE-5I. The mean physical component summary (PCS) score was 33.5 at baseline, 41.2 at 3 months, 40.8 at 6 months, and 42.0 at 12 months, and the mean mental component summary (MCS) scores were 45.6, 47.0, 50.0, and 50.1, respectively. PCS score was significantly greater at 3 months than at baseline (P = 0.035). MCS score was comparable at 3 months and at baseline, but was significantly greater at 6 and 12 months than at baseline (P = 0.033, P = 0.028, respectively). Thus, PCS score improved soon after initiation of therapy, and MCS score improved later.
Conclusions: Together, these results suggest that goal-oriented sequential combination therapy based on exercise capacity improves HRQOL in patients with PAH.
Conflict of interest statement
Akihiro Hirashiki used to belong to a department endowed by Actelion Pharmaceuticals Japan, Ltd. Both Takahisa Kondo, Naoki Okumura and Shiro Adachi belong to a department endowed by Actelion Pharmaceuticals Japan, Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulatory power and ventilatory power over time under goal-oriented sequential combination therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension.Pulm Circ. 2017 Apr-Jun;7(2):448-454. doi: 10.1177/2045893217703954. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Pulm Circ. 2017. PMID: 28597753 Free PMC article.
-
Macitentan Improves Health-Related Quality of Life for Patients With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Results From the Randomized Controlled SERAPHIN Trial.Chest. 2017 Jan;151(1):106-118. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2016.08.1473. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Chest. 2017. PMID: 27671974 Clinical Trial.
-
Quality of life as a prognostic marker in pulmonary arterial hypertension.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014 Aug 30;12:130. doi: 10.1186/s12955-014-0130-3. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014. PMID: 25176512 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Pulmonary arterial hypertension in patients with congenital heart disease: current issues and health care situation].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2013 Jun;138(23):1247-52. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1343189. Epub 2013 May 29. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2013. PMID: 23720182 Review. German.
-
Macitentan in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Focus on Combination Therapy in the SERAPHIN Trial.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2018 Feb;18(1):1-11. doi: 10.1007/s40256-017-0260-1. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29280064 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adaptation and validation of the quality of life assessment of the Cambridge pulmonary hypertension outcome review (CAMPHOR) for Brazil.J Patient Rep Outcomes. 2020 Jun 5;4(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s41687-020-00209-6. J Patient Rep Outcomes. 2020. PMID: 32504261 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Galie N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the joint task force for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) Eur Respir J. 2015;46(4):903–975. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01032-2015. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

