TCPA v3.0: An Integrative Platform to Explore the Pan-Cancer Analysis of Functional Proteomic Data
- PMID: 31201206
- PMCID: PMC6692772
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.RA118.001260
TCPA v3.0: An Integrative Platform to Explore the Pan-Cancer Analysis of Functional Proteomic Data
Abstract
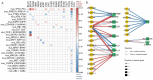
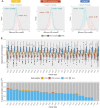
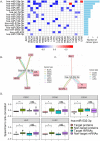
Reverse-phase protein arrays represent a powerful functional proteomics approach to characterizing cell signaling pathways and understanding their effects on cancer development. Using this platform, we have characterized ∼8,000 patient samples of 32 cancer types through The Cancer Genome Atlas and built a widely used, open-access bioinformatic resource, The Cancer Proteome Atlas (TCPA). To maximize the utility of TCPA, we have developed a new module called "TCGA Pan-Cancer Analysis," which provides comprehensive protein-centric analyses that integrate protein expression data and other TCGA data across cancer types. We further demonstrate the value of this module by examining the correlations of RPPA proteins with significantly mutated genes, assessing the predictive power of somatic copy-number alterations, DNA methylation, and mRNA on protein expression, inferring the regulatory effects of miRNAs on protein expression, constructing a co-expression network of proteins and pathways, and identifying clinically relevant protein markers. This upgraded TCPA (v3.0) will provide the cancer research community with a more powerful tool for studying functional proteomics and making translational impacts.
Keywords: Bioinformatics Software; Biomarker: Prognostic; Cancer Biology; Functional Proteomics; Gene Expression; Pan-Cancer Analysis; Pathway Analysis; Protein Array; Proteogenomics; TCGA.
© 2019 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
G.B.M. has sponsored research support from AstraZeneca, Critical Outcomes Technology, Karus, Illumina, Immunomet, Nanostring, Tarveda, and Immunomet and is on the Scientific Advisory Board for AstraZeneca, Critical Outcomes Technology, ImmunoMet, Ionis, Nuevolution, Symphogen, and Tarveda. H.L. is a shareholder and scientific advisor of Precision Scientific Ltd., (Beijing, China) and Eagle Nebula Inc
Figures




References
-
- Sheehan K. M., Calvert V. S., Kay E. W., Lu Y., Fishman D., Espina V., Aquino J., Speer R., Araujo R., Mills G. B., Liotta L. A., Petricoin E. F. 3rd, Wulfkuhle J. D. (2005) Use of reverse phase protein microarrays and reference standard development for molecular network analysis of metastatic ovarian carcinoma. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 4, 346–355 - PubMed
-
- Spurrier B., Ramalingam S., and Nishizuka S. (2008) Reverse-phase protein lysate microarrays for cell signaling analysis. Nat. Protoc. 3, 1796–1808 - PubMed
-
- Li J., Zhao W., Akbani R., Liu W., Ju Z., Ling S., Vellano C. P., Roebuck P., Yu Q., Eterovic A. K., Byers L. A., Davies M. A., Deng W., Gopal Y. N., Chen G., von Euw E. M., Slamon D., Conklin D., Heymach J. V., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D., Myers J. N., Lu Y., Mills G. B., and Liang H. (2017) Characterization of human cancer cell lines by reverse-phase protein arrays. Cancer Cell 31, 225–239 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

