The cell biology of the hepatocyte: A membrane trafficking machine
- PMID: 31201265
- PMCID: PMC6605791
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201903090
The cell biology of the hepatocyte: A membrane trafficking machine
Abstract
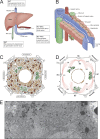
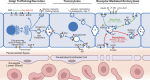
The liver performs numerous vital functions, including the detoxification of blood before access to the brain while simultaneously secreting and internalizing scores of proteins and lipids to maintain appropriate blood chemistry. Furthermore, the liver also synthesizes and secretes bile to enable the digestion of food. These diverse attributes are all performed by hepatocytes, the parenchymal cells of the liver. As predicted, these cells possess a remarkably well-developed and complex membrane trafficking machinery that is dedicated to moving specific cargos to their correct cellular locations. Importantly, while most epithelial cells secrete nascent proteins directionally toward a single lumen, the hepatocyte secretes both proteins and bile concomitantly at its basolateral and apical domains, respectively. In this Beyond the Cell review, we will detail these central features of the hepatocyte and highlight how membrane transport processes play a key role in healthy liver function and how they are affected by disease.
© 2019 Schulze et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cell polarity development and protein trafficking in hepatocytes lacking E-cadherin/beta-catenin-based adherens junctions.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Jun;18(6):2313-21. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-11-1040. Epub 2007 Apr 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17429067 Free PMC article.
-
The mitochondrial import gene tomm22 is specifically required for hepatocyte survival and provides a liver regeneration model.Dis Model Mech. 2010 Jul-Aug;3(7-8):486-95. doi: 10.1242/dmm.004390. Epub 2010 May 18. Dis Model Mech. 2010. PMID: 20483998 Free PMC article.
-
Pluripotent stem cell-derived bile canaliculi-forming hepatocytes to study genetic liver diseases involving hepatocyte polarity.J Hepatol. 2019 Aug;71(2):344-356. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.03.031. Epub 2019 Apr 6. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30965071
-
Mechanisms and functional features of polarized membrane traffic in epithelial and hepatic cells.Biochem J. 1998 Dec 1;336 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):257-69. doi: 10.1042/bj3360257. Biochem J. 1998. PMID: 9820799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and functional hepatocyte polarity and liver disease.J Hepatol. 2015 Oct;63(4):1023-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.06.015. Epub 2015 Jun 24. J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26116792 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current view of liver cancer cell-of-origin and proposed mechanisms precluding its proper determination.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Jan 6;23(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02843-0. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 36609378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Albumosomes formed by cytoplasmic pre-folding albumin maintain mitochondrial homeostasis and inhibit nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Jun 16;8(1):229. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01437-0. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37321990 Free PMC article.
-
Liver-secreted fluorescent blood plasma markers enable chronic imaging of the microcirculation.Cell Rep Methods. 2022 Sep 21;2(10):100302. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2022.100302. eCollection 2022 Oct 24. Cell Rep Methods. 2022. PMID: 36313804 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptors FXR and SHP regulate protein N-glycan modifications in the liver.Sci Adv. 2021 Apr 21;7(17):eabf4865. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abf4865. Print 2021 Apr. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 33883138 Free PMC article.
-
A method to generate perfusable physiologic-like vascular channels within a liver-on-chip model.Biomicrofluidics. 2023 Dec 4;17(6):064103. doi: 10.1063/5.0170606. eCollection 2023 Dec. Biomicrofluidics. 2023. PMID: 38058462 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

