The neuropeptide GsMTx4 inhibits a mechanosensitive BK channel through the voltage-dependent modification specific to mechano-gating
- PMID: 31201274
- PMCID: PMC6682741
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005511
The neuropeptide GsMTx4 inhibits a mechanosensitive BK channel through the voltage-dependent modification specific to mechano-gating
Abstract
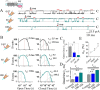
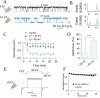
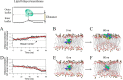
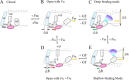
The cardiac mechanosensitive BK (Slo1) channels are gated by Ca2+, voltage, and membrane stretch. The neuropeptide GsMTx4 is a selective inhibitor of mechanosensitive (MS) channels. It has been reported to suppress stretch-induced cardiac fibrillation in the heart, but the mechanism underlying the specificity and even the targeting channel(s) in the heart remain elusive. Here, we report that GsMTx4 inhibits a stretch-activated BK channel (SAKcaC) in the heart through a modulation specific to mechano-gating. We show that membrane stretching increases while GsMTx4 decreases the open probability (Po) of SAKcaC. These effects were mostly abolished by the deletion of the STREX axis-regulated (STREX) exon located between RCK1 and RCK2 domains in BK channels. Single-channel kinetics analysis revealed that membrane stretch activates SAKcaC by prolonging the open-time duration (τO) and shortening the closed-time constant (τC). In contrast, GsMTx4 reversed the effects of membrane stretch, suggesting that GsMTx4 inhibits SAKcaC activity by interfering with mechano-gating of the channel. Moreover, GsMTx4 exerted stronger efficacy on SAKcaC under membrane-hyperpolarized/resting conditions. Molecular dynamics simulation study revealed that GsMTx4 appeared to have the ability to penetrate deeply within the bilayer, thus generating strong membrane deformation under the hyperpolarizing/resting conditions. Immunostaining results indicate that BK variants containing STREX are also expressed in mouse ventricular cardiomyocytes. Our results provide common mechanisms of peptide actions on MS channels and may give clues to therapeutic suppression of cardiac arrhythmias caused by excitatory currents through MS channels under hyper-mechanical stress in the heart.
Keywords: BK channel; arrhythmias; biophysics; gating; heart; inhibition mechanism; ion channel; kinetics; lipid–peptide interaction; mechanosensitive channel; molecular dynamics; patch clamp; peptides; single channel kinetics; structural model.
© 2019 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures








Similar articles
-
Two types of peptides derived from the neurotoxin GsMTx4 inhibit a mechanosensitive potassium channel by modifying the mechanogate.J Biol Chem. 2022 Sep;298(9):102326. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102326. Epub 2022 Aug 4. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35933015 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning the mechanosensitivity of a BK channel by changing the linker length.Cell Res. 2008 Aug;18(8):871-8. doi: 10.1038/cr.2008.88. Cell Res. 2008. PMID: 18663377
-
Membrane stretch and cytoplasmic Ca2+ independently modulate stretch-activated BK channel activity.J Biomech. 2010 Nov 16;43(15):3015-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2010.06.018. Epub 2010 Jul 29. J Biomech. 2010. PMID: 20673577
-
Stretch-activated BK channel and heart function.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2012 Oct-Nov;110(2-3):239-44. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2012.08.001. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 23281538 Review.
-
A BK (Slo1) channel journey from molecule to physiology.Channels (Austin). 2013 Nov-Dec;7(6):442-58. doi: 10.4161/chan.26242. Epub 2013 Sep 11. Channels (Austin). 2013. PMID: 24025517 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Piezo1 Is a Mechanosensor Channel in Central Nervous System Capillaries.Circ Res. 2022 May 13;130(10):1531-1546. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.320827. Epub 2022 Apr 6. Circ Res. 2022. PMID: 35382561 Free PMC article.
-
Piezo1 activation induces relaxation of the pudendal artery and corpus cavernosum.Front Physiol. 2023 Feb 10;14:998951. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.998951. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36846322 Free PMC article.
-
Piezo1 Affects Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis by Influencing pSmad3.Front Physiol. 2022 May 9;13:892089. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.892089. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35615665 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanobiological insight into brain diseases based on mechanosensitive channels: Common mechanisms and clinical potential.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Jun;30(6):e14809. doi: 10.1111/cns.14809. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 38923822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A synthetic peptide, derived from neurotoxin GsMTx4, acts as a non-opioid analgesic to alleviate mechanical and neuropathic pain through the TRPV4 channel.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025 Mar;15(3):1447-1462. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.028. Epub 2024 Dec 30. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025. PMID: 40370548 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

