Genomic signatures of heterokaryosis in the oomycete pathogen Bremia lactucae
- PMID: 31201315
- PMCID: PMC6570648
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-10550-0
Genomic signatures of heterokaryosis in the oomycete pathogen Bremia lactucae
Abstract
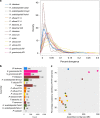
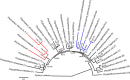
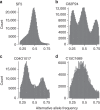
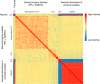
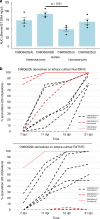
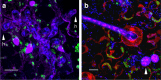
Lettuce downy mildew caused by Bremia lactucae is the most important disease of lettuce globally. This oomycete is highly variable and rapidly overcomes resistance genes and fungicides. The use of multiple read types results in a high-quality, near-chromosome-scale, consensus assembly. Flow cytometry plus resequencing of 30 field isolates, 37 sexual offspring, and 19 asexual derivatives from single multinucleate sporangia demonstrates a high incidence of heterokaryosis in B. lactucae. Heterokaryosis has phenotypic consequences on fitness that may include an increased sporulation rate and qualitative differences in virulence. Therefore, selection should be considered as acting on a population of nuclei within coenocytic mycelia. This provides evolutionary flexibility to the pathogen enabling rapid adaptation to different repertoires of host resistance genes and other challenges. The advantages of asexual persistence of heterokaryons may have been one of the drivers of selection that resulted in the loss of uninucleate zoospores in multiple downy mildews.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effector-mediated discovery of a novel resistance gene against Bremia lactucae in a nonhost lettuce species.New Phytol. 2017 Nov;216(3):915-926. doi: 10.1111/nph.14741. Epub 2017 Aug 21. New Phytol. 2017. PMID: 28833168 Free PMC article.
-
Host-induced gene silencing inhibits the biotrophic pathogen causing downy mildew of lettuce.Plant Biotechnol J. 2015 Sep;13(7):875-83. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12307. Epub 2014 Dec 9. Plant Biotechnol J. 2015. PMID: 25487781
-
Recognition of lettuce downy mildew effector BLR38 in Lactuca serriola LS102 requires two unlinked loci.Mol Plant Pathol. 2019 Feb;20(2):240-253. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12751. Epub 2018 Nov 6. Mol Plant Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30251420 Free PMC article.
-
Studying Wild Plant Pathosystems to Understand Crop Plant Pathosystems: Status, Gaps, Challenges, and Perspectives.Phytopathology. 2023 Mar;113(3):365-380. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-01-22-0018-PER. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Phytopathology. 2023. PMID: 36256745 Review.
-
Recent advances in oomycete genomics.Adv Genet. 2020;105:175-228. doi: 10.1016/bs.adgen.2020.03.001. Epub 2020 Apr 25. Adv Genet. 2020. PMID: 32560787 Review.
Cited by
-
The genome of the oomycete Peronosclerospora sorghi, a cosmopolitan pathogen of maize and sorghum, is inflated with dispersed pseudogenes.G3 (Bethesda). 2023 Mar 9;13(3):jkac340. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac340. G3 (Bethesda). 2023. PMID: 36592124 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Assessment of the Secretome Responsible for Host Adaptation of the Legume Root Pathogen Aphanomyces euteiches.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Jan 17;8(1):88. doi: 10.3390/jof8010088. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35050028 Free PMC article.
-
Long transposon-rich centromeres in an oomycete reveal divergence of centromere features in Stramenopila-Alveolata-Rhizaria lineages.PLoS Genet. 2020 Mar 9;16(3):e1008646. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008646. eCollection 2020 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32150559 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogeography and population structure of the global, wide host-range hybrid pathogen Phytophthora × cambivora.IMA Fungus. 2023 Feb 23;14(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s43008-023-00109-6. IMA Fungus. 2023. PMID: 36823663 Free PMC article.
-
Worldwide forest surveys reveal forty-three new species in Phytophthora major Clade 2 with fundamental implications for the evolution and biogeography of the genus and global plant biosecurity.Stud Mycol. 2024 Mar;107:251-388. doi: 10.3114/sim.2024.107.04. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Stud Mycol. 2024. PMID: 38600961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crute IR, Harrison JM. Studies on the inheritance of resistance to metalaxyl in Bremia lactucae and on the stability and fitness of field isolates. Plant Pathol. 1988;37:231–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3059.1988.tb02069.x. - DOI
-
- Schettini T, Legg E, Michelmore R. Insensitivity to metalaxyl in California populations of Bremia lactucae and resistance of California lettuce cultivars to downy mildew. Phytopathology. 1991;81:64–70. doi: 10.1094/Phyto-81-64. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

