Convergent allostery in ribonucleotide reductase
- PMID: 31201319
- PMCID: PMC6572854
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-10568-4
Convergent allostery in ribonucleotide reductase
Abstract
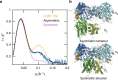
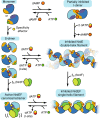
Ribonucleotide reductases (RNRs) use a conserved radical-based mechanism to catalyze the conversion of ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides. Within the RNR family, class Ib RNRs are notable for being largely restricted to bacteria, including many pathogens, and for lacking an evolutionarily mobile ATP-cone domain that allosterically controls overall activity. In this study, we report the emergence of a distinct and unexpected mechanism of activity regulation in the sole RNR of the model organism Bacillus subtilis. Using a hypothesis-driven structural approach that combines the strengths of small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), crystallography, and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), we describe the reversible interconversion of six unique structures, including a flexible active tetramer and two inhibited helical filaments. These structures reveal the conformational gymnastics necessary for RNR activity and the molecular basis for its control via an evolutionarily convergent form of allostery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM081393/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM124166/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM124847/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM081393/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)/International
- P41 GM103485/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM124847/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)/International
- GM103485/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)/International
- DMR-1332208/National Science Foundation (NSF)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

