The hydrolase LpqI primes mycobacterial peptidoglycan recycling
- PMID: 31201321
- PMCID: PMC6572805
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-10586-2
The hydrolase LpqI primes mycobacterial peptidoglycan recycling
Abstract
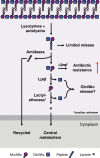
Growth and division by most bacteria requires remodelling and cleavage of their cell wall. A byproduct of this process is the generation of free peptidoglycan (PG) fragments known as muropeptides, which are recycled in many model organisms. Bacteria and hosts can harness the unique nature of muropeptides as a signal for cell wall damage and infection, respectively. Despite this critical role for muropeptides, it has long been thought that pathogenic mycobacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis do not recycle their PG. Herein we show that M. tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis BCG are able to recycle components of their PG. We demonstrate that the core mycobacterial gene lpqI, encodes an authentic NagZ β-N-acetylglucosaminidase and that it is essential for PG-derived amino sugar recycling via an unusual pathway. Together these data provide a critical first step in understanding how mycobacteria recycle their peptidoglycan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/S010122/1/RCUK | Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)/International
- BB/N011945/1/RCUK | Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)/International
- MR/S000542/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/S000542/1/RCUK | MRC | Medical Research Foundation/International
- MR/K012118/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

