Adamts17 is involved in skeletogenesis through modulation of BMP-Smad1/5/8 pathway
- PMID: 31201465
- PMCID: PMC11105417
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-019-03188-0
Adamts17 is involved in skeletogenesis through modulation of BMP-Smad1/5/8 pathway
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Adamts17 is involved in skeletogenesis through modulation of BMP‑Smad1/5/8 pathway.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Dec;76(23):4811-4812. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03325-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31620828 Free PMC article.
Abstract
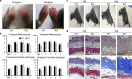
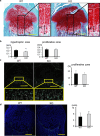
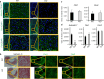
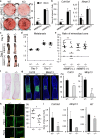
Fibrillin microfibrils are ubiquitous elements of extracellular matrix assemblies that play crucial roles in regulating the bioavailability of growth factors of the transforming growth factor beta superfamily. Recently, several "a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs" (ADAMTS) proteins were shown to regulate fibrillin microfibril function. Among them, ADAMTS17 is the causative gene of Weill-Marchesani syndrome (WMS) and Weill-Marchesani-like syndrome, of which common symptoms are ectopia lentis and short stature. ADAMTS17 has also been linked to height variation in humans; however, the molecular mechanisms whereby ADAMTS17 regulates skeletal growth remain unknown. Here, we generated Adamts17-/- mice to examine the role of Adamts17 in skeletogenesis. Adamts17-/- mice recapitulated WMS, showing shorter long bones, brachydactyly, and thick skin. The hypertrophic zone of the growth plate in Adamts17-/- mice was shortened, with enhanced fibrillin-2 deposition, suggesting increased incorporation of fibrillin-2 into microfibrils. Comprehensive gene expression analysis of growth plates using laser microdissection and RNA sequencing indicated alteration of the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling pathway after Adamts17 knockout. Consistent with this, phospho-Smad1 levels were downregulated in the hypertrophic zone of the growth plate and in Adamts17-/- primary chondrocytes. Delayed terminal differentiation of Adamts17-/- chondrocytes, observed both in primary chondrocyte and primordial metatarsal cultures, and was prevented by BMP treatment. Our data indicated that Adamts17 is involved in skeletal formation by modulating BMP-Smad1/5/8 pathway, possibly through inhibiting the incorporation of fibrillin-2 into microfibrils. Our findings will contribute to further understanding of disease mechanisms and will facilitate the development of therapeutic interventions for WMS.
Keywords: Adamts17; Fibrillin; Microfibril; Skeletal formation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ADAMTS10-mediated tissue disruption in Weill-Marchesani syndrome.Hum Mol Genet. 2018 Nov 1;27(21):3675-3687. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy276. Hum Mol Genet. 2018. PMID: 30060141 Free PMC article.
-
Adamts10 inactivation in mice leads to persistence of ocular microfibrils subsequent to reduced fibrillin-2 cleavage.Matrix Biol. 2019 Apr;77:117-128. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.09.004. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Matrix Biol. 2019. PMID: 30201140 Free PMC article.
-
Unusual life cycle and impact on microfibril assembly of ADAMTS17, a secreted metalloprotease mutated in genetic eye disease.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 8;7:41871. doi: 10.1038/srep41871. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28176809 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and functional linkage between ADAMTS superfamily proteins and fibrillin-1: a novel mechanism influencing microfibril assembly and function.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011 Oct;68(19):3137-48. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0780-9. Epub 2011 Aug 20. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21858451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ADAMTS proteins as modulators of microfibril formation and function.Matrix Biol. 2015 Sep;47:34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2015.05.004. Epub 2015 May 7. Matrix Biol. 2015. PMID: 25957949 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Zinn's zonule.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021 May;82:100902. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100902. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 32980533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Novel Loci Associated with Body Conformation Traits in Qinchuan Cattle.Animals (Basel). 2023 Nov 23;13(23):3628. doi: 10.3390/ani13233628. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38066979 Free PMC article.
-
O-fucosylation of thrombospondin type 1 repeats is essential for ECM remodeling and signaling during bone development.Matrix Biol. 2022 Mar;107:77-96. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2022.02.002. Epub 2022 Feb 12. Matrix Biol. 2022. PMID: 35167946 Free PMC article.
-
Gentiopicroside promotes the osteogenesis of bone mesenchymal stem cells by modulation of β-catenin-BMP2 signalling pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Dec;25(23):10825-10836. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16410. Epub 2021 Nov 15. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34783166 Free PMC article.
-
Key Proteins for Regeneration in A. mexicanum: Transcriptomic Insights From Aged and Juvenile Limbs.Scientifica (Cairo). 2024 Nov 14;2024:5460694. doi: 10.1155/2024/5460694. eCollection 2024. Scientifica (Cairo). 2024. PMID: 39575453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Le Goff C, Mahaut C, Wang LW, Allali S, Abhyankar A, Jensen S, Zylberberg L, Collod-Beroud G, Bonnet D, Alanay Y, Brady AF, Cordier MP, Devriendt K, Genevieve D, Kiper PO, Kitoh H, Krakow D, Lynch SA, Le Merrer M, Megarbane A, Mortier G, Odent S, Polak M, Rohrbach M, Sillence D, Stolte-Dijkstra I, Superti-Furga A, Rimoin DL, Topouchian V, Unger S, Zabel B, Bole-Feysot C, Nitschke P, Handford P, Casanova JL, Boileau C, Apte SS, Munnich A, Cormier-Daire V. Mutations in the TGFbeta binding-protein-like domain 5 of FBN1 are responsible for acromicric and geleophysic dysplasias. Am J Hum Genet. 2011;89(1):7–14. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.05.012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 16K10810/Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
- 17K10924/Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
- 17H04311/Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

