Bioactivation of the tobacco carcinogens 4-aminobiphenyl (4-ABP) and 2-amino-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole (AαC) in human bladder RT4 cells
- PMID: 31203411
- PMCID: PMC6714057
- DOI: 10.1007/s00204-019-02486-7
Bioactivation of the tobacco carcinogens 4-aminobiphenyl (4-ABP) and 2-amino-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole (AαC) in human bladder RT4 cells
Abstract
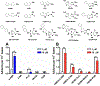
Occupational and tobacco exposure to aromatic amines (AAs) including 4-aminobiphenyl (4-ABP) and 2-naphthylamine (2-NA) are associated with bladder cancer (BC) risk. Several epidemiological studies have also reported a possible role for structurally related heterocyclic aromatic amines (HAAs) formed in tobacco smoke or cooked meats with BC risk. We had screened for DNA adducts of 4-ABP, 2-NA, and several prominent HAAs formed in tobacco smoke or grilled meats including 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (PhIP), 2-amino-3,8-dimethylmidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline (MeIQx), and 2-amino-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole (AαC) in the bladder DNA of BC patients, using liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. We detected DNA adducts of 4-ABP, but not adducts of the other carcinogens. In this study, we have examined the capacity of RT4 cells, an epithelial human bladder cell line, to bioactivate AAs and HAAs to DNA damaging agents, which may contribute to BC. 4-ABP and AαC formed DNA adducts, but DNA adducts of 2-NA, PhIP, and MeIQx were not detected. 4-ABP DNA adducts were formed at tenfold higher levels than AαC adducts. Pretreatment of RT4 cells with α-naphthoflavone (1-10 µM), a specific cytochrome P450 1 (CYP1) inhibitor, decreased AαC adduct formation by 50% but did not affect the level of 4-ABP adducts. However, cell pretreatment with 8-methoxypsoralen (0.1-1 µM), a potent inhibitor of CYP2A, resulted in a 90% decrease of 4-ABP DNA adducts levels. These data signify that CYP2A and CYP1A isoforms expressed in the target urothelium bioactivate 4-ABP and AαC, respectively, and may be a critical feature of aromatic amine-induced urinary bladder carcinogenesis. The bioactivation of other tobacco and environmental AAs by bladder CYPs and their ensuing bladder DNA damage warrants further study.
Keywords: 2-Amino-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole; 4-Aminobiphenyl; Aromatic amines; Bladder cancer; DNA adduct; Heterocyclic aromatic amines.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest:
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Figures
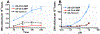
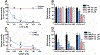
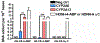
Similar articles
-
DNA adducts of the tobacco carcinogens 2-amino-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole and 4-aminobiphenyl are formed at environmental exposure levels and persist in human hepatocytes.Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Sep 16;26(9):1367-77. doi: 10.1021/tx4002226. Epub 2013 Aug 16. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23898916 Free PMC article.
-
DNA adduct formation of 4-aminobiphenyl and heterocyclic aromatic amines in human hepatocytes.Chem Res Toxicol. 2011 Jun 20;24(6):913-25. doi: 10.1021/tx200091y. Epub 2011 Apr 19. Chem Res Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21456541 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of Hemoglobin and White Blood Cell DNA Adducts of the Tobacco Carcinogens 2-Amino-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole and 4-Aminobiphenyl Formed in Humans by Nanoflow Liquid Chromatography/Ion Trap Multistage Mass Spectrometry.Chem Res Toxicol. 2017 Jun 19;30(6):1333-1343. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.7b00072. Epub 2017 May 25. Chem Res Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28493705 Free PMC article.
-
Black (air-cured) and blond (flue-cured) tobacco cancer risk. IV: Molecular dosimetry studies implicate aromatic amines as bladder carcinogens.Eur J Cancer. 1993;29A(8):1199-207. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(05)80315-6. Eur J Cancer. 1993. PMID: 8518034 Review.
-
Two food-borne heterocyclic amines: metabolism and DNA adduct formation of amino-alpha-carbolines.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2005 Mar;49(3):263-73. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200400061. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2005. PMID: 15704238 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of the carcinogen aristolochic acid I (AA-I) in human bladder RT4 cells.Arch Toxicol. 2021 Jun;95(6):2189-2199. doi: 10.1007/s00204-021-03059-3. Epub 2021 May 3. Arch Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33938965 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Damage and Oxidative Stress of Tobacco Smoke Condensate in Human Bladder Epithelial Cells.Chem Res Toxicol. 2022 Oct 17;35(10):1863-1880. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.2c00153. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Chem Res Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35877975 Free PMC article.
-
TRAIL-mediated signaling in bladder cancer: realization of clinical efficacy of TRAIL-based therapeutics in medical oncology.Med Oncol. 2023 Jul 11;40(8):236. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02078-7. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37432489 Review.
-
Analysis of six aromatic amines in the mainstream smoke of tobacco products.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022 Jun;414(14):4227-4234. doi: 10.1007/s00216-022-04075-7. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022. PMID: 35410388 Free PMC article.
-
Tobacco Smoke Is a Major Source of Aromatic Amine Exposure in U.S. Adults: 2013-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES).Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2023 May 17:OF1-OF9. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-23-0071. Online ahead of print. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2023. PMID: 37195136 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balbi JC, Larrinaga MT, De Stefani E, et al. (2001) Foods and risk of bladder cancer: a case-control study in Uruguay. Eur J Cancer Prev 10(5):453–8 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

