Project Spraoi: a two-year longitudinal study on the effectiveness of a school-based nutrition and physical activity intervention on dietary intake, nutritional knowledge and markers of health of Irish schoolchildren
- PMID: 31203819
- PMCID: PMC10260632
- DOI: 10.1017/S1368980019001368
Project Spraoi: a two-year longitudinal study on the effectiveness of a school-based nutrition and physical activity intervention on dietary intake, nutritional knowledge and markers of health of Irish schoolchildren
Abstract
Objective: To assess the effectiveness of a nutrition and physical activity (PA) intervention on dietary intake (DI), nutritional knowledge (NK), blood pressure (BP), anthropometric measures and cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) of schoolchildren.
Design: Longitudinal study. DI, NK, BMI, waist-to-height ratio (WHtR), BP and CRF were all measured/calculated prior to (October 2014) and at the end of (June 2016) intervention delivery.
Setting: Two primary schools (one intervention and one control), Cork, Ireland.
Participants: Six-year-olds (n 49; mean age = 6·09 (sd 0·33) years) and 10-year-olds (n 52; mean age = 9·90 (sd 0·37) years).
Results: There was a large and a moderate statistically significant difference between the change in systolic (P = 0·005, effect size (ES) = 0·165) and diastolic BP (P = 0·023, ES = 0·116), respectively, for 10-year-olds in the intervention and control groups. There was also a large statistically significant difference between the change in WHtR (P = 0·0005, ES = 0·386) and a moderate statistically significant difference between the change in NK (P = 0·027, ES = 0·107) for 10-year-olds in the intervention and control groups. There was a large statistically significant difference between the change in percentage of energy from protein in 10-year-old females (P = 0·021, ES = 0·276) in the intervention and control groups.
Conclusions: Project Spraoi is Ireland's first ever school-based intervention that has been evaluated and proven effective in improving DI, NK, WHtR and BP in older primary-school children in one intervention school.
Keywords: Children; Nutrition and physical activity intervention; Obesity prevention.
Figures
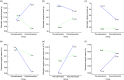
 , intervention group;
, intervention group;  , control group
, control groupReferences
-
- World Health Organization (2009) Interventions on diet and physical activity: what works: summary report. https://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/summary-report-09.pdf (accessed August 2017). - PubMed
-
- Weiss R, Dziura J, Burgert TS et al.. (2004) Obesity and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. N Engl J Med 350, 2362–2374. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (2003) Diet, Nutrition and the Prevention of Chronic Diseases. Joint WHO/FAO Expert Consultation. WHO Technical Report Series no. 916. Geneva: WHO. - PubMed
-
- Waters E, de Silva-Sanigorski A, Burford BJ et al.. (2011) Interventions for preventing obesity in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev issue 12, CD001871. - PubMed
-
- Perry CK, Garside H, Morones S et al.. (2012) Physical activity interventions for adolescents: an ecological perspective. J Prim Prev 33, 111–135. - PubMed

