Venetoclax-based therapies for acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 31203996
- PMCID: PMC6581210
- DOI: 10.1016/j.beha.2019.05.008
Venetoclax-based therapies for acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
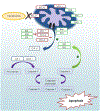
The prognosis of adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remains poor, with the long-term survival rate less than 50%. However, the current paradigms of treatment are changing through a better understanding of the disease genetics and pathophysiology. Since 2017, eight new drugs have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of AML, including the FLT3 inhibitors midostaurin and gilteritinib, the IDH inhibitors ivosidenib and enasidenib, the anti-CD33 monoclonal antibody gemtuzumab ozogamicin, liposomal daunorubicin and cytarabine, the hedgehog pathway inhibitor glasdegib and the BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax. Preclinical data demonstrated the anti-leukemic efficacy of venetoclax in AML and its synergy when combined with hypomethylating agents or chemotherapy agents. Clinical trials have demonstrated the clinical benefit of venetoclax-based therapies in newly diagnosed AML, leading to the recent FDA approval of venetoclax in combination with hypomethylating agents or low-dose cytarabine for older adults with newly diagnosed AML. Herein, we focus on the role of single-agent BCL-2 inhibition in AML and review the clinical studies of venetoclax-based combination regimens and the evolving mechanisms of resistance.
Keywords: Acute myeloid leukemia; Hypomethylating agents; Low-intensity chemotherapy; Venetoclax.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Conflicts of Interest:
The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Krapcho M, Neyman N, Aminou R, Waldron W et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review 1975–2007 National Cancer Institute SEER Cancer Statistics Review 1975–2007 National Cancer Institute. Cancer. 2010;1975–2007.
-
- Bose P, Vachhani P, Cortes JE. Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Curr Treat Options in Oncol. 2017;18(17). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

