Human Antibodies that Slow Erythrocyte Invasion Potentiate Malaria-Neutralizing Antibodies
- PMID: 31204103
- PMCID: PMC6602525
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.025
Human Antibodies that Slow Erythrocyte Invasion Potentiate Malaria-Neutralizing Antibodies
Abstract
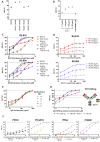
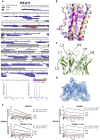
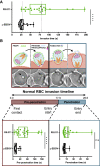
The Plasmodium falciparum reticulocyte-binding protein homolog 5 (PfRH5) is the leading target for next-generation vaccines against the disease-causing blood-stage of malaria. However, little is known about how human antibodies confer functional immunity against this antigen. We isolated a panel of human monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against PfRH5 from peripheral blood B cells from vaccinees in the first clinical trial of a PfRH5-based vaccine. We identified a subset of mAbs with neutralizing activity that bind to three distinct sites and another subset of mAbs that are non-functional, or even antagonistic to neutralizing antibodies. We also identify the epitope of a novel group of non-neutralizing antibodies that significantly reduce the speed of red blood cell invasion by the merozoite, thereby potentiating the effect of all neutralizing PfRH5 antibodies as well as synergizing with antibodies targeting other malaria invasion proteins. Our results provide a roadmap for structure-guided vaccine development to maximize antibody efficacy against blood-stage malaria.
Keywords: RH5; X-ray crystallography; blood-stage; live-cell microscopy; malaria; merozoite; monoclonal antibody; neutralization; structural vaccinology; synergy.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


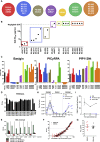
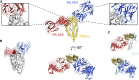
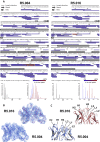
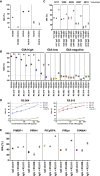
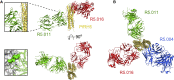
Comment in
-
Structure Solves the Problem with Malaria Merozoite Vaccines.Trends Parasitol. 2019 Nov;35(11):855-857. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2019.09.004. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Trends Parasitol. 2019. PMID: 31623952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afonine P.V., Grosse-Kunstleve R.W., Echols N., Headd J.J., Moriarty N.W., Mustyakimov M., Terwilliger T.C., Urzhumtsev A., Zwart P.H., Adams P.D. Towards automated crystallographic structure refinement with phenix.refine. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2012;68:352–367. - PMC - PubMed
- Afonine, P.V., Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W., Echols, N., Headd, J.J., Moriarty, N.W., Mustyakimov, M., Terwilliger, T.C., Urzhumtsev, A., Zwart, P.H., and Adams, P.D. (2012). Towards automated crystallographic structure refinement with phenix.refine. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 68, 352-367. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balazs A.B., Chen J., Hong C.M., Rao D.S., Yang L., Baltimore D. Antibody-based protection against HIV infection by vectored immunoprophylaxis. Nature. 2011;481:81–84. - PMC - PubMed
- Balazs, A.B., Chen, J., Hong, C.M., Rao, D.S., Yang, L., and Baltimore, D. (2011). Antibody-based protection against HIV infection by vectored immunoprophylaxis. Nature 481, 81-84. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bates J.T., Keefer C.J., Slaughter J.C., Kulp D.W., Schief W.R., Crowe J.E., Jr. Escape from neutralization by the respiratory syncytial virus-specific neutralizing monoclonal antibody palivizumab is driven by changes in on-rate of binding to the fusion protein. Virology. 2014;454-455:139–144. - PMC - PubMed
- Bates, J.T., Keefer, C.J., Slaughter, J.C., Kulp, D.W., Schief, W.R., and Crowe, J.E., Jr. (2014). Escape from neutralization by the respiratory syncytial virus-specific neutralizing monoclonal antibody palivizumab is driven by changes in on-rate of binding to the fusion protein. Virology 454-455, 139-144. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baum J., Chen L., Healer J., Lopaticki S., Boyle M., Triglia T., Ehlgen F., Ralph S.A., Beeson J.G., Cowman A.F. Reticulocyte-binding protein homologue 5 - an essential adhesin involved in invasion of human erythrocytes by Plasmodium falciparum. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009;39:371–380. - PubMed
- Baum, J., Chen, L., Healer, J., Lopaticki, S., Boyle, M., Triglia, T., Ehlgen, F., Ralph, S.A., Beeson, J.G., and Cowman, A.F. (2009). Reticulocyte-binding protein homologue 5 - an essential adhesin involved in invasion of human erythrocytes by Plasmodium falciparum. Int. J. Parasitol. 39, 371-380. - PubMed
-
- Beernink P.T., Welsch J.A., Bar-Lev M., Koeberling O., Comanducci M., Granoff D.M. Fine antigenic specificity and cooperative bactericidal activity of monoclonal antibodies directed at the meningococcal vaccine candidate factor h-binding protein. Infect. Immun. 2008;76:4232–4240. - PMC - PubMed
- Beernink, P.T., Welsch, J.A., Bar-Lev, M., Koeberling, O., Comanducci, M., and Granoff, D.M. (2008). Fine antigenic specificity and cooperative bactericidal activity of monoclonal antibodies directed at the meningococcal vaccine candidate factor h-binding protein. Infect. Immun. 76, 4232-4240. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

