Trans-Cinnamaldehyde Inhibits IL-1 β-Stimulated Inflammation in Chondrocytes by Suppressing NF- κ B and p38-JNK Pathways and Exerts Chondrocyte Protective Effects in a Rat Model of Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 31205941
- PMCID: PMC6530235
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/4039472
Trans-Cinnamaldehyde Inhibits IL-1 β-Stimulated Inflammation in Chondrocytes by Suppressing NF- κ B and p38-JNK Pathways and Exerts Chondrocyte Protective Effects in a Rat Model of Osteoarthritis
Abstract
Objective: Trans-cinnamaldehyde (TCA), a compound from Cinnamomum cassia Presl, has been reported to have anti-inflammatory effect. However, its effect on cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis is unclear. This study is designed to examine the effects of TCA on cartilage in vitro and in vivo.
Material and methods: SW1353 cells and human primary chondrocytes were treated with varying concentrations of TCA (2-20 μg/ml) for 2 h followed by IL-1β stimulation. Cell viability was examined by the MTT assay. Expression of MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-13, ADAMTS-4, and ADAMTS-5 was examined by Western blot and RT-qPCR. Monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)-induced OA was established in rats to assess the chondrocyte protective effects of intraperitoneal injection of TCA (50 mg/kg).
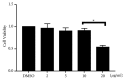
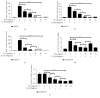
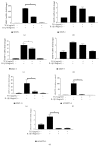
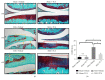
Results: TCA at a concentration of 10 μg/ml had no significant effect on cell viability. MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-13, ADAMTS-4, and ADAMTS-5 were decreased by TCA 2-10 μg/ml in a dose-dependent manner (all P<0.05). Pretreatment with TCA decreased the degradation of IκBα and increased the expression of p-IκBα, indicating that NF-κB inactivation was induced by TCA in IL-1β-stimulated SW1353 cells. Pretreatment with TCA decreased the levels of p-p38 and p-JNK, while the levels of p-ERK were not significantly affected. TCA 10 μg/ml significantly decreased expression levels of MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-13, ADAMTS-4, and ADAMTS-5. In vivo results showed that TCA alleviated cartilage destruction and the OARSI scores.
Conclusion: TCA possesses anti-inflammatory effect in vitro and exerts chondrocyte protective effects in vivo, in which NF-κB and p38-JNK were involved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Aqueous extract of Codium fragile alleviates osteoarthritis through the MAPK/NF-κB pathways in IL-1β-induced rat primary chondrocytes and a rat osteoarthritis model.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jan;97:264-270. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.130. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29091874
-
Mori folium inhibits interleukin-1β-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinases and inflammatory mediators by suppressing the activation of NF-κB and p38 MAPK in SW1353 human chondrocytes.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Feb;37(2):452-60. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2443. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26707272
-
The protective impact of Trans-Cinnamaldehyde (TCA) against the IL-1b induced inflammation in in vitro osteoarthritis model by regulating PI3K/AKT pathways.Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2020;58(4):264-271. doi: 10.5603/FHC.a2020.0025. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2020. PMID: 33118610
-
Cinnamaldehyde-Mediated Suppression of MMP-13, COX-2, and IL-6 Through MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Inhibition in Chondrocytes and Synoviocytes Under Inflammatory Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 30;25(23):12914. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312914. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684628 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory signaling in cartilage: MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways in chondrocytes and the use of inhibitors for research into pathogenesis and therapy of osteoarthritis.Curr Drug Targets. 2007 Feb;8(2):305-13. doi: 10.2174/138945007779940115. Curr Drug Targets. 2007. PMID: 17305508 Review.
Cited by
-
Small molecules of herbal origin for osteoarthritis treatment: in vitro and in vivo evidence.Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 May 11;24(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02785-y. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35545776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Danshensu inhibits the IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in chondrocytes and osteoarthritis possibly via suppressing NF-κB signaling pathway.Mol Med. 2021 Jul 20;27(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00329-9. Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34284715 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the Therapeutic Potential of Nano-Delivered Functional Foods in Chronic Respiratory Diseases.Nutrients. 2022 Sep 16;14(18):3828. doi: 10.3390/nu14183828. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36145202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue Engineering Strategies for Treating Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head.Bioengineering (Basel). 2021 Dec 2;8(12):200. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering8120200. Bioengineering (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34940353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aromatic Plants as Potential Resources to Combat Osteoarthritis.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(10):1434-1465. doi: 10.2174/0113862073267213231004094629. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 37861046 Review.
References
-
- Gelber A. C. In the clinic. Osteoarthritis. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2014;161(1):ITC1–16. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

