The Impact of "Churn" on Plasma HIV Burden Within a Population Under Care
- PMID: 31205974
- PMCID: PMC6557304
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofz203
The Impact of "Churn" on Plasma HIV Burden Within a Population Under Care
Abstract
Background: Cross-sectional reporting of viral suppression rates within a population underestimates the community viral load (VL) burden. Longitudinal approaches, while addressing cumulative effects, may still underestimate viral burden if "churn" (movement in and out of care) is not incorporated. We examined the impact of churn on the cumulative community HIV viral burden.
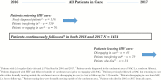
Methods: All HIV+ patients followed in 2016-2017 at the Southern Alberta Clinic (Calgary, Canada) were categorized as follows: (1) in continuous care, (2) newly diagnosed, (3) diagnosed elsewhere transferring care, (4) returning to care, (5) lost-to-follow-up, (6) moved care elsewhere, or (7) died. Patient days were classified by VL as suppressed (≤200copies/ml), unsuppressed (>200 copies/ml), and transmittable (>1500 copies/ml).
Results: Of 1934 patients, 78.4% had suppressed VL; 21.4% had ≥1 unsuppressed VL, and 18.7% ≥1 transmittable VL. Of 1 276 507 total patient days in care, 92.1% were spent suppressed, 7.9% unsuppressed (101 459 days), and 6.4% (81 847 days) transmittable. 88.7% of category 1 patients had suppressed VL, 11.3% ≥1 unsuppressed VL, and 8.9% ever a transmittable VL. Of category 2 patients, 90% became suppressed on treatment (mean - 62 days). 38.5% of category 3 patients presented with a transmittable VL. Category 4 and 5 patients combined had high rates of unsuppressed (54.5%) and transmittable (51.2%) VL and, while representing only 6.2% of all patients, they accounted for 37.1% of unsuppressed and 41.5% of all transmittable days.
Conclusion: Focus on VL of patients continuously in care misses those with unsuppressed and transmittable VL in a community. Patients moving in and out of care pose an underappreciated risk for HIV transmissions.
Keywords: AIDS; Canada; HIV; viral suppression; antiretroviral therapy; churn.
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS. 90-90-90. An ambitious treatment target to help end the AIDS epidemic. Available at: http://www.unaids.org/en/resources/909090. Accessed May 6, 2019.
-
- Simmons RD, Ciancio BC, Kall MM, et al. . Ten-year mortality trends among persons diagnosed with HIV infection in England and Wales in the era of antiretroviral therapy: AIDS remains a silent killer. HIV Med 2013; 14:596–604. - PubMed
-
- Attia S, Egger M, Müller M, et al. . Sexual transmission of HIV according to viral load and antiretroviral therapy: systematic review and meta-analysis. AIDS 2009; 23:1397–404. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources