Downregulation of JKAP is correlated with elevated disease risk, advanced disease severity, higher inflammation, and poor survival in sepsis
- PMID: 31206807
- PMCID: PMC6757113
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.22945
Downregulation of JKAP is correlated with elevated disease risk, advanced disease severity, higher inflammation, and poor survival in sepsis
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to explore the association of JKAP with sepsis risk and investigate its correlation with disease severity, inflammatory cytokines, and survival in sepsis patients.
Methods: A hundred and one sepsis patients along with 100 healthy controls were enrolled, and their blood serum samples were collected for JKAP and inflammatory cytokines measurement by enzyme-linked immunoassay. The difference in serum JKAP between sepsis patients and healthy controls was determined. Among sepsis patients, the correlation of JKAP with disease severity, laboratory indexes, inflammatory cytokines, 28-day mortality, and accumulating survival was analyzed.
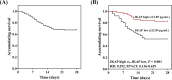
Results: JNK pathway-associated phosphatase level was decreased in sepsis patients compared with healthy controls and presented with good value in predicting decreased sepsis risk (AUC = 0.896 [95% CI: 0.851-0.941]). And its low expression was associated with advanced disease severity (APACHE II score and SOFA score) and systemic inflammation (CRP, PCT, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-17) in sepsis patients. Additionally, JKAP level was decreased in deaths compared with survivors and had good value in distinguishing deaths from survivors (AUC = 0.742 [95% CI: 0.636-0.849]). Further, Kaplan-Meier curve analysis disclosed that JKAP high expression predicted more prolonged accumulating survival in sepsis patients.
Conclusion: JNK pathway-associated phosphatase is of good value in predicting lower sepsis risk, and its downregulation correlates with advanced disease severity, higher level of systemic inflammation, and poor survival in sepsis patients.
Keywords: JNK pathway-associated phosphatase; disease risk; inflammation; sepsis; survival.
© 2019 The Authors Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Clinical value of serum JKAP in acute ischemic stroke patients.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Apr;36(4):e24270. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24270. Epub 2022 Mar 10. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35274367 Free PMC article.
-
The correlation between Jun N-terminal kinase pathway-associated phosphatase and Th1 cell or Th17 cell in sepsis and their potential roles in clinical sepsis management.Ir J Med Sci. 2021 Aug;190(3):1173-1181. doi: 10.1007/s11845-020-02382-5. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Ir J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33083958 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of the phosphatase JKAP/DUSP22 in T cells as a potential new biomarker of systemic lupus erythematosus nephritis.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 6;7(36):57593-57605. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11419. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27557500 Free PMC article.
-
JNK pathway-associated phosphatase associates with rheumatoid arthritis risk, disease activity, and its longitudinal elevation relates to etanercept treatment response.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Apr;35(4):e23709. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23709. Epub 2021 Feb 6. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 33547838 Free PMC article.
-
JNK Pathway-Associated Phosphatase as a Serum Marker for Disease Activity and Treatment Outcome of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis.Tohoku J Exp Med. 2021 Jan;253(1):19-28. doi: 10.1620/tjem.253.19. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2021. PMID: 33441511
Cited by
-
Dual specificity phosphatase 22 relates to skin lesion degree and biologics history, while its longitudinal elevation during treatment reflects better outcome in psoriasis patients.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Feb;36(2):e24199. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24199. Epub 2021 Dec 31. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 34973040 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical value of serum JKAP in acute ischemic stroke patients.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Apr;36(4):e24270. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24270. Epub 2022 Mar 10. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35274367 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Methylation Analysis to Unravel Altered Genetic Pathways Underlying Early Onset and Late Onset Neonatal Sepsis. A Pilot Study.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 15;12:622599. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.622599. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33659006 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrates (IRS-1 and IRS-2) is attenuated following cecal ligation and puncture in mice.Mol Med. 2023 Aug 7;29(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00703-9. Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37550630 Free PMC article.
-
The correlation between Jun N-terminal kinase pathway-associated phosphatase and Th1 cell or Th17 cell in sepsis and their potential roles in clinical sepsis management.Ir J Med Sci. 2021 Aug;190(3):1173-1181. doi: 10.1007/s11845-020-02382-5. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Ir J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33083958 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

