MicroRNA-301b-3p contributes to tumour growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma by repressing vestigial like family member 4
- PMID: 31207037
- PMCID: PMC6653225
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14361
MicroRNA-301b-3p contributes to tumour growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma by repressing vestigial like family member 4
Abstract
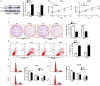
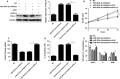
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are key regulators in the tumour growth and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Increasing evidence suggests that miR-301b-3p functions as a driver in various types of human cancer. However, the expression pattern of miR-301b-3p and its functional role as well as underlying molecular mechanism in HCC remain poorly known. Our study found that miR-301b-3p expression was significantly up-regulated in HCC tissues compared to adjacent non-tumour tissues. Clinical association analysis revealed that the high level of miR-301b-3p closely correlated with large tumour size and advanced tumour-node-metastasis stages. Importantly, the high miR-301b-3p level predicted a prominent poorer overall survival of HCC patients. Knockdown of miR-301b-3p suppressed cell proliferation, led to cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase and induced apoptosis of Huh7 and Hep3B cells. Furthermore, miR-301b-3p knockdown suppressed tumour growth of HCC in mice. Mechanistically, miR-301b-3p directly bond to 3'UTR of vestigial like family member 4 (VGLL4) and negatively regulated its expression. The expression of VGLL4 mRNA was down-regulated and inversely correlated with miR-301b-3p level in HCC tissues. Notably, VGLL4 knockdown markedly repressed cell proliferation, resulted in G2/M phase arrest and promoted apoptosis of HCC cells. Accordingly, VGLL4 silencing rescued miR-301b-3p knockdown attenuated HCC cell proliferation, cell cycle progression and apoptosis resistance. Collectively, our results suggest that miR-301b-3p is highly expressed in HCC. miR-301b-3p facilitates cell proliferation, promotes cell cycle progression and inhibits apoptosis of HCC cells by repressing VGLL4.
Keywords: G2/M phase arrest; VGLL4; apoptosis; cell proliferation; hepatocellular carcinoma; miR-301b-3p.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
miR-1307-3p promotes tumor growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by repressing DAB2 interacting protein.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Sep;117:109055. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109055. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31176165
-
MicroRNA-519c-3p promotes tumor growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting BTG3.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Oct;118:109267. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109267. Epub 2019 Aug 3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31387005
-
HOXA-AS2 Promotes Proliferation and Induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via the miR-520c-3p/GPC3 Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(6):2124-2138. doi: 10.1159/000495056. Epub 2018 Nov 9. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30415263
-
The Role of the MiR-181 Family in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cells. 2024 Jul 31;13(15):1289. doi: 10.3390/cells13151289. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39120319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growing Evidence of Exosomal MicroRNA-Related Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Nov 27;2020:4501454. doi: 10.1155/2020/4501454. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33313314 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of cuproptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma using multi-omics reveals a comprehensive HCC landscape and the immune patterns of cuproptosis.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 2;12:1009036. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1009036. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36408192 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation, characterisation, and in vitro cancer-suppression function of RNA nanoparticles carrying miR-301b-3p Inhibitor.IET Nanobiotechnol. 2023 May;17(3):224-233. doi: 10.1049/nbt2.12120. Epub 2023 Mar 9. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36892102 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 contributes to lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and apoptosis of human middle ear epithelial cells via regulating the miR-301b-3p/TLR4 axis.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Dec;22(6):1360. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10795. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34659506 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-Inducible Ubiquitin Specific Peptidase 13 Contributes to Tumor Growth and Metastasis via Enhancing the Toll-Like Receptor 4/Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response Gene 88/Nuclear Factor-κB Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Oct 19;8:587389. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.587389. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33195243 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA LINC01123 promotes the proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by modulating the miR-34a-5p/TUFT1 axis.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Jun 5;16(13):2296-2305. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.45457. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32760198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115‐132. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7‐30. - PubMed
-
- Dou C, Zhou Z, Xu Q, et al. Hypoxia‐induced TUFT1 promotes the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by activating the Ca(2+)/PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncogene. 2019;38:1239‐1255. - PubMed
-
- Wong CM, Tsang FH, Ng IO. Non‐coding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular functions and pathological implications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:137‐151. - PubMed
-
- Lv H, Lv G, Han Q, Yang W, Wang H. Noncoding RNAs in liver cancer stem cells: the big impact of little things. Cancer Lett. 2018;418:51‐63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

