The role of Sevenless in Drosophila R7 photoreceptor specification
- PMID: 31207209
- PMCID: PMC6726512
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2019.06.007
The role of Sevenless in Drosophila R7 photoreceptor specification
Abstract
Sevenless (Sev) is a Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK) that is required for the specification of the Drosophila R7 photoreceptor. Other Drosophila photoreceptors are specified by the action of another RTK; the Drosophila EGF Receptor (DER). Why Sev is required specifically in the R7 precursor, and the exact role it plays in the cell's fate assignment have long remained unclear. Notch (N) signaling plays many roles in R7 specification, one of which is to prevent DER activity from establishing the photoreceptor fate. Our current model of Sev function is that it hyperactivates the RTK pathway in the R7 precursor to overcome the N-imposed block on photoreceptor specification. From this perspective DER and Sev are viewed as engaging the same transduction machinery, the only difference between them being the level of pathway activation that they induce. To test this model, we generated a Sev/DER chimera in which the intracellular domain of Sev is replaced with that of DER. This chimerical receptor acts indistinguishably from Sev itself; a result that is entirely consistent with the two RTKs sharing identical transduction abilities. A long-standing question in regard to Sev is the function of a hydrophobic domain some 60 amino acids from the initiating Methionine. If this represents a transmembrane domain, it would endow Sev with N-terminal intracellular sequences through which it could engage internal transduction pathways. However, we find that this domain acts as an internal signal peptide, and that there is no Sev N-terminal intracellular domain. phyllopod (phyl) is the target gene of the RTK pathway, and we show that R7 precursors are selectively lost when phyl gene function is mildly compromised, and that other photoreceptors are removed when the gene function is further reduced. This result adds a key piece of evidence for the hyperactivation of the RTK pathway in the R7 precursor. To facilitate the hyperactivation of the RTK pathway, Sev is expressed at high levels. However, when we express DER at the levels at which Sev is expressed, strong gain-of-function effects result, consistent with ligand-independent activation of the receptor. This highlights another key feature of Sev; that it is expressed at high levels yet remains strictly ligand dependent. Finally, we find that activated Sev can rescue R3/4 photoreceptors when their DER function is abrogated. These results are collectively consistent with Sev and DER activating the same transduction machinery, with Sev generating a pathway hyperactivation to overcome the N-imposed block to photoreceptor specification in R7 precursors.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
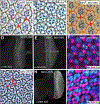
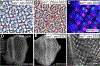
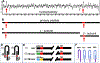
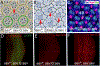
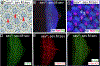
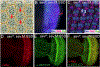
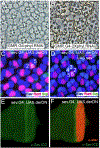
Similar articles
-
Three distinct roles for notch in Drosophila R7 photoreceptor specification.PLoS Biol. 2011 Aug;9(8):e1001132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001132. Epub 2011 Aug 23. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21886484 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding a Cell's Fate: How Notch and receptor tyrosine kinase signals specify the Drosophila R7 photoreceptor.Dev Biol. 2025 Mar;519:21-29. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2024.12.001. Epub 2024 Dec 7. Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 39653132
-
SOCS36E specifically interferes with Sevenless signaling during Drosophila eye development.Dev Biol. 2009 Feb 1;326(1):212-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.11.014. Epub 2008 Nov 30. Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19083999
-
Stop and go: antagonistic signals in the specification of the Drosophila R7 photoreceptor viewed from an evolutionary perspective.Fly (Austin). 2012 Oct-Dec;6(4):228-33. doi: 10.4161/fly.21102. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Fly (Austin). 2012. PMID: 22878552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling mechanisms in induction of the R7 photoreceptor in the developing Drosophila retina.Bioessays. 1994 Apr;16(4):237-44. doi: 10.1002/bies.950160406. Bioessays. 1994. PMID: 8031300 Review.
Cited by
-
Deep conservation complemented by novelty and innovation in the insect eye ground plan.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jan 7;122(1):e2416562122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2416562122. Epub 2024 Dec 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 39793041 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the interaction between the Drosophila RTK Sevenless (dROS1) and the GPCR BOSS.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 18;16(1):808. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-55943-6. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39827240 Free PMC article.
-
Insect opsins and evo-devo: what have we learned in 25 years?Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022 Oct 24;377(1862):20210288. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2021.0288. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36058243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structures and pH-dependent dimerization of the sevenless receptor tyrosine kinase.Mol Cell. 2024 Dec 5;84(23):4677-4690.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.10.017. Epub 2024 Nov 6. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 39510067
-
Drosophila as a Model for Infectious Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 8;22(5):2724. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052724. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33800390 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- BASLER K, CHRISTEN B & HAFEN E 1991. Ligand-independent activation of the sevenless receptor tyrosine kinase changes the fate of cells in the developing Drosophila eye. Cell, 64,1069–81. - PubMed
-
- BONFINI L,.KARLOVICH CA, DASGUPTA C& BANERJEE U 1992. The Son of sevenless gene product: a putative activator of Ras. Science, 255, 603–6. - PubMed
-
- CARTHEW RW & RUBIN GM 1990. seven in absentia, a gene required for specification of R7 cell fate in the Drosophila eye. Cell, 63, 561–77. - PubMed
-
- COOPER MT & BRAY SJ 2000. R7 photoreceptor specification requires Notch activity. Current biology: CB, 10,1507–10. - PubMed
-
- DICKSON BJ, DOMINGUEZ M, VAN DER STRATEN A& HAFEN E 1995. Control of Drosophila photoreceptor cell fates by phyllopod, a novel nuclear protein acting downstream of the Raf kinase. Cell, 80, 453–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

