TOX transcriptionally and epigenetically programs CD8+ T cell exhaustion
- PMID: 31207603
- PMCID: PMC6713202
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1325-x
TOX transcriptionally and epigenetically programs CD8+ T cell exhaustion
Abstract
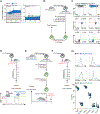
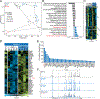
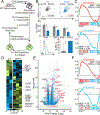
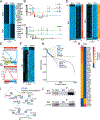
Exhausted CD8+ T (Tex) cells in chronic infections and cancer have limited effector function, high co-expression of inhibitory receptors and extensive transcriptional changes compared with effector (Teff) or memory (Tmem) CD8+ T cells. Tex cells are important clinical targets of checkpoint blockade and other immunotherapies. Epigenetically, Tex cells are a distinct immune subset, with a unique chromatin landscape compared with Teff and Tmem cells. However, the mechanisms that govern the transcriptional and epigenetic development of Tex cells remain unknown. Here we identify the HMG-box transcription factor TOX as a central regulator of Tex cells in mice. TOX is largely dispensable for the formation of Teff and Tmem cells, but it is critical for exhaustion: in the absence of TOX, Tex cells do not form. TOX is induced by calcineurin and NFAT2, and operates in a feed-forward loop in which it becomes calcineurin-independent and sustained in Tex cells. Robust expression of TOX therefore results in commitment to Tex cells by translating persistent stimulation into a distinct Tex cell transcriptional and epigenetic developmental program.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
O.K. is an employee of Arsenal Biosciences. R.K.A. serves as a consultant for Sprint Biosciences, Immunacell and Array Pharmaceuticals and is a founder of Pinpoint Therapeutics. T.C.M. is an advisor to and/or receives honoraria from Aduro, Array, BMS, Incyte, Merck, Regeneron. S.L.B receives research funding from Celgene. E.J.W. receives honoraria, consulting fees and/or research support from BMS, Celgene, Dynavax, Eli Lilly, Elstar, Merck, MedImmune, Pieris, Roche, Surface Oncology, and KyMab. E.J.W. is a founder of Arsenal Biosciences. E.J.W. has a patent licensing agreement for the PD-1 pathway.
Figures








References
-
- Barber DL et al. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature 439, 682–687 (2005). - PubMed
METHODS REFERENCES
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

