Effect of Postoperative Oral Intake on Prognosis for Esophageal Cancer
- PMID: 31207910
- PMCID: PMC6627190
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11061338
Effect of Postoperative Oral Intake on Prognosis for Esophageal Cancer
Abstract
Background: Patients undergoing surgery for esophageal cancer are at risk of prolonged hospital stay for postoperative malnutrition. Postoperative early oral feeing is a part of the "enhanced recovery after surgery protocol" for coping with this risk. However, the usefulness of early oral intake during perioperatively is questionable.
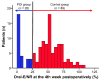
Methods: In total, 117 patients treated surgically for esophageal cancer were analyzed in the study. We assessed the oral energy sufficiency rate per nutritional requirement (oral-E/NR) at the fourth week postoperatively and classified the patients into two groups: Poor oral intake group (POI group; <25% oral-E/NR) and the control group (≥25% oral-E/NR). We analyzed the relationship among postoperative oral intake and prognoses.
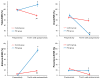
Results: The POI group had worse postoperative nutritional status and a lower survival rate than the control group. In a multivariate analysis, <25% oral-E/NR was one of the independent factors contributing to negative outcomes postoperatively (adjusted hazard ratio: 2.70, 95% confidence interval: 1.30-5.61).
Conclusions: In patients undergoing surgery for esophageal cancer, poor postoperative oral intake negatively affected not only on their postoperative nutritional status but also their overall prognosis. It is necessary to improve the adequacy of oral intake postoperatively for patients with esophageal cancer.
Keywords: administration; energy intake; esophagectomy; nutrition therapy; outcomes research/quality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Pedersen H., Hansen H.S., Cederqvist C., Løber J. The prognostic significance of weight loss and its integration in stage-grouping of oesophageal cancer. Acta Chir. Scand. 1982;148:363–366. - PubMed
-
- Onodera T., Goseki N., Kosaki G. Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery of malnourished cancer patients. J. Jpn. Surg. Soc. 1984;85:1001–1005. - PubMed
-
- Guo S.Z., Shen Q., Zhang H.B. Expression and significance of immunosuppressive acidic protein (IAP) in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 1994;16:125–127. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

