Integrative Analyses of mRNA Expression Profile Reveal the Involvement of IGF2BP1 in Chicken Adipogenesis
- PMID: 31208008
- PMCID: PMC6627201
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20122923
Integrative Analyses of mRNA Expression Profile Reveal the Involvement of IGF2BP1 in Chicken Adipogenesis
Abstract
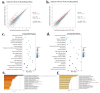
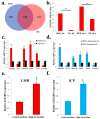
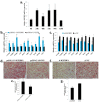
Excessive abdominal fat deposition is an issue with general concern in broiler production, especially for Chinese native chicken breeds. A high-fat diet (HFD) can induce body weight gained and excessive fat deposition, and genes and pathways participate in fat metabolism and adipogenesis would be influenced by HFD. In order to reveal the main genes and pathways involved in chicken abdominal fat deposition, we used HFD and normal diet (ND) to feed a Chinese native chicken breed, respectively. Results showed that HFD can increase abdominal fat deposition and induce adipocyte hypertrophy. Additionally, we used RNA-sequencing to identify the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between HFD and ND chickens in liver and abdominal fat. By analyzed these DEGs, we found that the many DEGs were enriched in fat metabolism related pathways, such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) signaling, fat digestion and absorption, extracellular matrix (ECM)-receptor interaction, and steroid hormone biosynthesis. Notably, the expression of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1), which is a binding protein of IGF2 mRNA, was found to be induced in liver and abdominal fat by HFD. Ectopic expression of IGF2BP1 in chicken liver-related cell line Leghorn strain M chicken hepatoma (LMH) cell revealed that IGF2BP1 can regulate the expression of genes associated with fatty acid metabolism. In chicken preadipocytes (ICP cell line), we found that IGF2BP1 can promote adipocyte proliferation and differentiation, and the lipid droplet content would be increased by overexpression of IGF2BP1. Taken together, this study provides new insights into understanding the genes and pathways involved in abdominal fat deposition of Chinese native broiler, and IGF2BP1 is an important candidate gene for the study of fat metabolism and adipogenesis in chicken.
Keywords: Chinese native broiler; IGF2BP1; abdominal fat deposition; adipogenesis; differentially expressed gene; high-fat diet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Integrative Analyses of mRNA Expression Profile Reveal SOCS2 and CISH Play Important Roles in GHR Mutation-Induced Excessive Abdominal Fat Deposition in the Sex-Linked Dwarf Chicken.Front Genet. 2021 Jan 14;11:610605. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.610605. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33519913 Free PMC article.
-
[The cell cycle pathway regulates chicken abdominal fat deposition as revealed by transcriptome sequencing].Yi Chuan. 2019 Oct 20;41(10):962-973. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-098. Yi Chuan. 2019. PMID: 31624058 Chinese.
-
Identification of differentially expressed genes and pathways between intramuscular and abdominal fat-derived preadipocyte differentiation of chickens in vitro.BMC Genomics. 2019 Oct 15;20(1):743. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6116-0. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31615399 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Regulation of Lipogenesis, Adipogenesis and Fat Deposition in Chicken.Genes (Basel). 2021 Mar 13;12(3):414. doi: 10.3390/genes12030414. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors affecting adipose tissue development in chickens: A review.Poult Sci. 2017 Oct 1;96(10):3687-3699. doi: 10.3382/ps/pex184. Poult Sci. 2017. PMID: 28938790 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrative Analyses of mRNA Expression Profile Reveal SOCS2 and CISH Play Important Roles in GHR Mutation-Induced Excessive Abdominal Fat Deposition in the Sex-Linked Dwarf Chicken.Front Genet. 2021 Jan 14;11:610605. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.610605. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33519913 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary bile acids supplementation decreases hepatic fat deposition with the involvement of altered gut microbiota and liver bile acids profile in broiler chickens.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 13;15(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s40104-024-01071-y. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39135090 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms and expressions of ADSL, MC4R and CAPN1 genes and their effects on economic traits in Egyptian chicken breeds.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Dec 10;51(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08999-w. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 38071695 Free PMC article.
-
Chicken Protein S Gene Regulates Adipogenesis and Affects Abdominal Fat Deposition.Animals (Basel). 2022 Aug 11;12(16):2046. doi: 10.3390/ani12162046. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009634 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of the KLF Gene Family in Chicken: Characterization and Expression Profile.Animals (Basel). 2023 Apr 22;13(9):1429. doi: 10.3390/ani13091429. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37174466 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

