Rho GTPases in the Physiology and Pathophysiology of Peripheral Sensory Neurons
- PMID: 31208035
- PMCID: PMC6627758
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8060591
Rho GTPases in the Physiology and Pathophysiology of Peripheral Sensory Neurons
Abstract
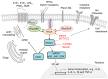
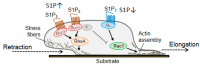
Numerous experimental studies demonstrate that the Ras homolog family of guanosine triphosphate hydrolases (Rho GTPases) Ras homolog family member A (RhoA), Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1) and cell division cycle 42 (Cdc42) are important regulators in somatosensory neurons, where they elicit changes in the cellular cytoskeleton and are involved in diverse biological processes during development, differentiation, survival and regeneration. This review summarizes the status of research regarding the expression and the role of the Rho GTPases in peripheral sensory neurons and how these small proteins are involved in development and outgrowth of sensory neurons, as well as in neuronal regeneration after injury, inflammation and pain perception. In sensory neurons, Rho GTPases are activated by various extracellular signals through membrane receptors and elicit their action through a wide range of downstream effectors, such as Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) or mixed-lineage kinase (MLK). While RhoA is implicated in the assembly of stress fibres and focal adhesions and inhibits neuronal outgrowth through growth cone collapse, Rac1 and Cdc42 promote neuronal development, differentiation and neuroregeneration. The functions of Rho GTPases are critically important in the peripheral somatosensory system; however, their signalling interconnections and partially antagonistic actions are not yet fully understood.
Keywords: Rho GTPases; actin cytoskeleton; development; inflammation; neurite outgrowth; neuroregeneration; pain; sensory neurons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RhoE stimulates neurite-like outgrowth in PC12 cells through inhibition of the RhoA/ROCK-I signalling.J Neurochem. 2010 Feb;112(4):1074-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06526.x. Epub 2009 Dec 3. J Neurochem. 2010. PMID: 19968760
-
Galanin stimulates neurite outgrowth from sensory neurons by inhibition of Cdc42 and Rho GTPases and activation of cofilin.J Neurochem. 2013 Oct;127(2):199-208. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12379. Epub 2013 Aug 22. J Neurochem. 2013. PMID: 23895321 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse roles of Rho family GTPases in neuronal development, survival, and death.Front Biosci. 2008 Jan 1;13:657-76. doi: 10.2741/2710. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 17981578 Review.
-
Abl tyrosine kinase promotes dendrogenesis by inducing actin cytoskeletal rearrangements in cooperation with Rho family small GTPases in hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci. 2004 Sep 29;24(39):8510-21. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1264-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15456825 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of phosphorylation pathways by p21 GTPases. The p21 Ras-related Rho subfamily and its role in phosphorylation signalling pathways.Eur J Biochem. 1996 Dec 1;242(2):171-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0171r.x. Eur J Biochem. 1996. PMID: 8973630 Review.
Cited by
-
Recurrent oxidant treatment induces dysregulation in the brain transcriptome of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) smolts.Toxicol Rep. 2022 Jun 23;9:1461-1471. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2022.06.009. eCollection 2022. Toxicol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36518465 Free PMC article.
-
MMP-9 Signaling Pathways That Engage Rho GTPases in Brain Plasticity.Cells. 2021 Jan 15;10(1):166. doi: 10.3390/cells10010166. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33467671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chloride - The Underrated Ion in Nociceptors.Front Neurosci. 2020 Apr 8;14:287. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00287. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32322187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels Play a Central Role in Caenorhabditis elegans Response to Noxious Heat.Neurochem Res. 2025 Jun 27;50(4):215. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04445-4. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40571785
-
Evaluation of an Intravitreal Rho-Associated Kinase Inhibitor Depot Formulation in a Rat Model of Diabetic Retinopathy.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jul 21;13(8):1105. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081105. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34452066 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

