A Comparison Study on the Arsenate Adsorption Behavior of Calcium-Bearing Materials
- PMID: 31208107
- PMCID: PMC6631780
- DOI: 10.3390/ma12121936
A Comparison Study on the Arsenate Adsorption Behavior of Calcium-Bearing Materials
Abstract
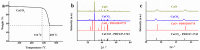
The calcium-bearing adsorbents are widely used in the treatment of arsenic-containing wastewater due to their excellent treatment effect and economy. In order to obtain high-efficient adsorbents for arsenate (As(V)) removal, the adsorption behavior of calcium oxide (CaO), calcium fluoride (CaF2) and calcium carbonate (CaCO3) on As(V) in aqueous solution at different concentrations were explored. The adsorption mechanism was also explored based on surface characteristics: morphology, specific surface area, as well as their effective calcium content. Not only that, the chemical stability of these materials was further studied. Results exhibited that the As(V) removal capability of these materials is in the following order, CaO > CaF2 > CaCO3. When CaO served as an absorbent, As(V) with initial concentration of 0.2 mg/L can be reduced to 0.383 × 10-3 mg/L in 10 min. Moreover, the capabilities of CaO, CaF2 and CaCO3 for removing As(V) are positively correlated with their effective calcium content in aqueous solution, which provide the basis for selecting calcium-bearing materials with excellently comprehensive properties for the field of As(V) removal in aqueous solution. What's more, all three materials exhibit great chemical stability after adsorption of As(V).
Keywords: As(V); adsorption mechanism; adsorption properties; calcium-bearing materials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Preparation and performance of arsenate (V) adsorbents derived from concrete wastes.Waste Manag. 2014 Oct;34(10):1829-35. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2014.01.001. Epub 2014 Jan 25. Waste Manag. 2014. PMID: 24472713
-
Synthesis of nano-scale zero-valent iron-reduced graphene oxide-silica nano-composites for the efficient removal of arsenic from aqueous solutions.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Nov;26(32):33507-33516. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06320-6. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31529346
-
Adsorption of arsenate and arsenite by iron-treated activated carbon and zeolites: effects of pH, temperature, and ionic strength.J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2005;40(4):723-49. doi: 10.1081/ese-200048254. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2005. PMID: 15792296
-
Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) based materials as emerging adsorbents for the removal of dyes and heavy metals - A review.Sci Total Environ. 2020 May 15;717:135070. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135070. Epub 2019 Nov 23. Sci Total Environ. 2020. PMID: 31839314 Review.
-
Rationally designed calcium carbonate multifunctional trap for contaminants adsorption.Sci Total Environ. 2023 Dec 10;903:166142. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166142. Epub 2023 Aug 12. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 37574061 Review.
Cited by
-
Adsorption of Heavy Metals Ions from Mining Metallurgical Tailings Leachate Using a Shell-Based Adsorbent: Characterization, Kinetics and Isotherm Studies.Materials (Basel). 2022 Aug 2;15(15):5315. doi: 10.3390/ma15155315. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35955251 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of Arsenic(V) from wastewater using calcined eggshells as a cost-effective adsorbent.Heliyon. 2025 Feb 6;11(3):e42505. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42505. eCollection 2025 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 40007776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saxena A., Kumar S., Gole P. Source mineral for the release of arsenic in the groundwater of Karanda Block, Ghazipur District, Uttar Pradesh. J. Geol. Soc. India. 2014;84:590–596. doi: 10.1007/s12594-014-0166-3. - DOI
-
- Tareq M. Source and characteristic of fluorescence humic substances in arsenic polluted groundwater of Bangladesh. J. Chin. Chem. Soc.-Taip. 2014;61:770–773. doi: 10.1002/jccs.201400060. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

