p-Coumaric Acid Has Protective Effects against Mutant Copper-Zinc Superoxide Dismutase 1 via the Activation of Autophagy in N2a Cells
- PMID: 31208129
- PMCID: PMC6628046
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20122942
p-Coumaric Acid Has Protective Effects against Mutant Copper-Zinc Superoxide Dismutase 1 via the Activation of Autophagy in N2a Cells
Abstract
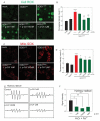
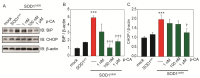
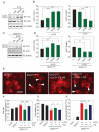
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by the selective death of motor neurons. In previous our study, an ethanol extract of Brazilian green propolis (EBGP) prevented mutant copper-zinc superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1mut)-induced neurotoxicity. This paper aims to reveal the effects of p-coumaric acid (p-CA), an active ingredient contained in EBGP, against SOD1mut-induced neurotoxicity. We found that p-CA reduced the accumulation of SOD1mut subcellular aggregation and prevented SOD1mut-associated neurotoxicity. Moreover, p-CA attenuated SOD1mut-induced oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress, which are significant features in ALS pathology. To examine the mechanism of neuroprotective effects, we focused on autophagy, and we found that p-CA induced autophagy. Additionally, the neuroprotective effects of p-CA were inhibited by chloroquine, an autophagy inhibiter. Therefore, these results obtained in this paper suggest that p-CA prevents SOD1mut-induced neurotoxicity through the activation of autophagy and provides a potential therapeutic approach for ALS.
Keywords: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; autophagy; copper–zinc superoxide dismutase 1; endoplasmic reticulum stress; oxidative stress; p-coumaric acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effects of Brazilian green propolis that contains flavonols against mutant copper-zinc superoxide dismutase-mediated toxicity.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 6;7(1):2882. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03115-y. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28588226 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of gem-dihydroperoxides against mutant copper‑zinc superoxide dismutase-mediated neurotoxicity.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2018 Oct;92:177-184. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2018.09.001. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30193933
-
γ-Oryzanol mitigates oxidative stress and prevents mutant SOD1-Related neurotoxicity in Drosophila and cell models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Dec 1;160:107777. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.107777. Epub 2019 Sep 12. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 31521619
-
SOD1 in neurotoxicity and its controversial roles in SOD1 mutation-negative ALS.Adv Biol Regul. 2016 Jan;60:95-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2015.10.006. Epub 2015 Oct 31. Adv Biol Regul. 2016. PMID: 26563614 Review.
-
Transgenic mouse model for familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with superoxide dismutase-1 mutation.Neuropathology. 2001 Mar;21(1):82-92. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1789.2001.00361.x. Neuropathology. 2001. PMID: 11304046 Review.
Cited by
-
Peanut (Arachis hypogaea) sprout prevents high-fat diet-induced cognitive impairment by improving mitochondrial function.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 13;12(1):6213. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10520-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35418581 Free PMC article.
-
The neuroprotective effects of activated α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor against mutant copper-zinc superoxide dismutase 1-mediated toxicity.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 17;10(1):22157. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79189-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33335227 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria and Endoplasmic Reticulum Contact Site as a Regulator of Proteostatic Stress Responses in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Bioessays. 2025 Jul;47(7):e70016. doi: 10.1002/bies.70016. Epub 2025 May 4. Bioessays. 2025. PMID: 40320859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural compounds modulate the autophagy with potential implication of stroke.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Jul;11(7):1708-1720. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.10.018. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 34386317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p-Coumaric acid alleviates neuronal damage in ischemic stroke mice by promoting BACH1 nuclear export and degradation.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 Aug;46(8):2136-2150. doi: 10.1038/s41401-025-01510-0. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 40087473
References
-
- Cheroni C., Marino M., Tortarolo M., Veglianese P., De Biasi S., Fontana E., Zuccarello L.V., Maynard C.J., Dantuma N.P., Bendotti C. Functional alterations of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in motor neurons of a mouse model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009;18:82–96. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn319. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

