p-Coumaric Acid Has Protective Effects against Mutant Copper-Zinc Superoxide Dismutase 1 via the Activation of Autophagy in N2a Cells
- PMID: 31208129
- PMCID: PMC6628046
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20122942
p-Coumaric Acid Has Protective Effects against Mutant Copper-Zinc Superoxide Dismutase 1 via the Activation of Autophagy in N2a Cells
Abstract
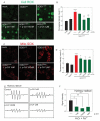
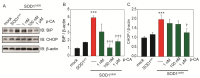
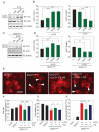
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by the selective death of motor neurons. In previous our study, an ethanol extract of Brazilian green propolis (EBGP) prevented mutant copper-zinc superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1mut)-induced neurotoxicity. This paper aims to reveal the effects of p-coumaric acid (p-CA), an active ingredient contained in EBGP, against SOD1mut-induced neurotoxicity. We found that p-CA reduced the accumulation of SOD1mut subcellular aggregation and prevented SOD1mut-associated neurotoxicity. Moreover, p-CA attenuated SOD1mut-induced oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress, which are significant features in ALS pathology. To examine the mechanism of neuroprotective effects, we focused on autophagy, and we found that p-CA induced autophagy. Additionally, the neuroprotective effects of p-CA were inhibited by chloroquine, an autophagy inhibiter. Therefore, these results obtained in this paper suggest that p-CA prevents SOD1mut-induced neurotoxicity through the activation of autophagy and provides a potential therapeutic approach for ALS.
Keywords: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; autophagy; copper–zinc superoxide dismutase 1; endoplasmic reticulum stress; oxidative stress; p-coumaric acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Cheroni C., Marino M., Tortarolo M., Veglianese P., De Biasi S., Fontana E., Zuccarello L.V., Maynard C.J., Dantuma N.P., Bendotti C. Functional alterations of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in motor neurons of a mouse model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009;18:82–96. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn319. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

