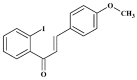
2-Iodo-4'-Methoxychalcone Attenuates Methylglyoxal-Induced Neurotoxicity by Activation of GLP-1 Receptor and Enhancement of Neurotrophic Signal, Antioxidant Defense and Glyoxalase Pathway
- PMID: 31208152
- PMCID: PMC6631972
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24122249
2-Iodo-4'-Methoxychalcone Attenuates Methylglyoxal-Induced Neurotoxicity by Activation of GLP-1 Receptor and Enhancement of Neurotrophic Signal, Antioxidant Defense and Glyoxalase Pathway
Abstract
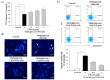
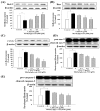
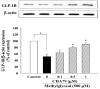
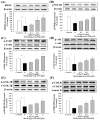
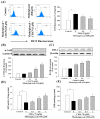
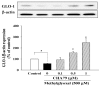
Methylglyoxal (MG) acts as a reactive precursor of advanced glycation end products (AGEs). This compound is often connected with pathologies such as diabetes, neurodegenerative processes and diseases of aging. 2-iodo-4'-methoxychalcone (CHA79), a synthetic halogen-containing chalcone derivative, has been reported its anti-diabetic activity. This study aims to investigate the potential protective capability of CHA79 against MG-mediated neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Results indicated CHA79 increased viability of cells and attenuated the rate of apoptosis in MG-exposed SH-SY5Y. CHA79 up-regulated expression of anti-apoptotic protein (Bcl-2) and down-regulated apoptotic proteins (Bax, cytochrome c, caspase-3, caspase-9). Moreover, CHA79 significantly up-regulated expression of neurotrophic factors, including glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R), brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), p75NTR, p-TrkB, p-Akt, p-GK-3β and p-CREB. CHA79 attenuated MG-induced ROS production and enhanced the antioxidant defense including nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), HO-1, SOD and GSH. Furthermore, CHA79 attenuated MG-induced reduction of glyoxalase-1 (GLO-1), a vital enzyme on removing AGE precursors. In conclusion, CHA79 is the first novel synthetic chalcone possessing the GLP-1R and GLO-1 activating properties. CHA 79 also exhibits neuroprotective effects against MG toxicity by enhancing neurotrophic signal, antioxidant defense and anti-apoptosis pathway.
Keywords: antioxidant defense; glyoxalase pathway; halogen-containing chalcones; methylglyoxal; neuroprotection; neurotrophic effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lo T.W., Westwood M.E., McLellan A.C., Selwood T., Thornalley P.J. Binding and modification of proteins by methylglyoxal under physiological conditions. A kinetic and mechanistic study with N alpha-acetylarginine, N alpha-acetylcysteine, and N alpha-acetyllysine, and bovine serum albumin. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:32299–32305. - PubMed
-
- Shimatani Y., Nodera H., Osaki Y., Banzrai C., Takayasu K., Endo S., Shibuta Y., Kaji R. Upregulation of axonal HCN current by methylglyoxal: Potential association with diabetic polyneuropathy. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015;126:2226–2232. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2015.02.058. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

