The Impact of Limbal Mesenchymal Stromal Cells on Healing of Acute Ocular Surface Wounds Is Improved by Pre-cultivation and Implantation in the Presence of Limbal Epithelial Cells
- PMID: 31208228
- PMCID: PMC6767890
- DOI: 10.1177/0963689719858577
The Impact of Limbal Mesenchymal Stromal Cells on Healing of Acute Ocular Surface Wounds Is Improved by Pre-cultivation and Implantation in the Presence of Limbal Epithelial Cells
Abstract
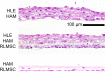
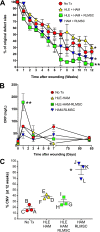
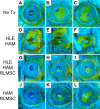
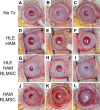
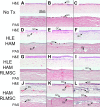
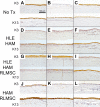
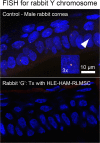
While limbal epithelial cells are used for treating ocular surface wounds, the therapeutic potential of mesenchymal cells cultivated from the limbal stroma (LMSC) is less clear. We have therefore examined the effects of LMSC when applied to acute ocular surface wounds. LMSC derived from male rabbits (RLMSC) were applied to the ocular surface of female rabbits immediately following removal of the corneal and limbal epithelium. Human amniotic membrane (HAM) was used as the vehicle for implanting the RLMSC. The effects of RLMSC were examined when applied alone (n = 3) and in conjunction with a stratified culture of human limbal epithelial cells (HLE) grown on the opposing surface of the HAM (n = 3). Outcomes were monitored over 3 months in comparison with animals receiving no treatment (n = 3) or treatment with HLE alone on HAM (n = 3). Animals treated with RLMSC (n = 6) displayed faster re-epithelialization (∼90% versus 70% healing after 12 weeks), with best results being observed when RLMSC were pre-cultivated and implanted in the presence of HLE (p < 0.01; 90% healing by 7 weeks). While all animals displayed conjunctival cells on the corneal surface (by presence of goblet cells and/or keratin 13 expression) and corneal neovascularization, evidence of corneal epithelial regeneration was observed in animals that received RLMSC in the presence of HLE (by staining for keratin 3 and the absence of goblet cells). Conversely, corneal neovascularization was significantly greater when RLMSC were applied in the absence of HLE (<0.05; 90% of cornea compared with 20-30% in other cohorts). Nevertheless, neither human nuclear antigen nor rabbit Y chromosome were detected within the regenerated epithelium. Our results demonstrate that while cultured LMSC encourage corneal re-epithelialization, healing is improved by the pre-cultivation and implantation of these mesenchymal cells in the presence of limbal epithelial cells.
Keywords: Algerbrush II; amniotic membrane; corneal neovascularization; limbal mesenchymal stromal cells; ocular surface; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Holland EJ. Management of limbal stem cell deficiency: a historical perspective, past, present, and future. Cornea. 2015;34(Suppl 10):S9–S15. - PubMed
-
- Ainscough SL, Linn ML, Barnard Z, Schwab IR, Harkin DG. Effects of fibroblast origin and phenotype on the proliferative potential of limbal epithelial progenitor cells. Exp Eye Res. 2011;92(1):10–19. - PubMed
-
- O’Callaghan AR, Morgan L, Daniels JT, Lewis MP. Human-derived feeder fibroblasts for the culture of epithelial cells for clinical use. Regen Med. 2016;11(6):529–543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

