Secretion of fibronectin by human pancreatic stellate cells promotes chemoresistance to gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer cells
- PMID: 31208372
- PMCID: PMC6580453
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-5803-1
Secretion of fibronectin by human pancreatic stellate cells promotes chemoresistance to gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer cells
Abstract
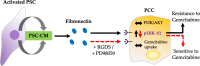
Background: Gemcitabine remains a cornerstone in chemotherapy of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) despite suboptimal clinical effects that are partly due to the development of chemoresistance. Pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs) of the tumor stroma are known to interact with pancreatic cancer cells (PCCs) and influence the progression of PDAC through a complex network of signaling molecules that involve extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins. To understand tumor-stroma interactions regulating chemosensitivity, the role of PSC-secreted fibronectin (FN) in the development of gemcitabine resistance in PDAC was examined.
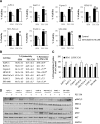
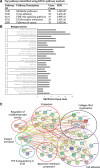
Methods: PSC cultures obtained from ten different human PDAC tumors were co-cultured with PCC lines (AsPC-1, BxPC-3, Capan-2, HPAF-II, MIA PaCa-2, PANC-1 and SW-1990) either directly, or indirectly via incubation with PSC-conditioned medium (PSC-CM). Gemcitabine dose response cytotoxicity was determined using MTT based cell viability assays. Protein expression was assessed by western blotting and immunofluorescence. PSC-CM secretome analysis was performed by proteomics-based LC-MS/MS, and FN content in PSC-CM was determined with ELISA. Radiolabeled gemcitabine was used to determine the capacity of PCCs to uptake the drug.
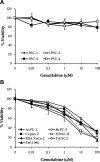
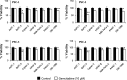
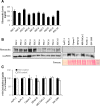
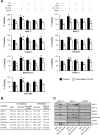
Results: In both direct and indirect co-culture, PSCs induced varying degrees of resistance to the cytotoxic effects of gemcitabine among all cancer cell lines examined. A variable degree of increased phosphorylation of ERK1/2 was observed across all PCC lines upon incubation with PSC-CM, while activation of AKT was not detected. Secretome analysis of PSC-CM identified 796 different proteins, including several ECM-related proteins such as FN and collagens. Soluble FN content in PSC-CM was detected in the range 175-350 ng/ml. Neither FN nor PSC-CM showed any effect on PCC uptake capacity of gemcitabine. PCCs grown on FN-coated surface displayed higher resistance to gemcitabine compared to cells grown on non-coated surface. Furthermore, a FN inhibitor, synthetic Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser (RGDS) peptide significantly inhibited PSC-CM-induced chemoresistance in PCCs via downregulation of ERK1/2 phosphorylation.
Conclusions: The findings of this study suggest that FN secreted by PSCs in the ECM plays a key role in the development of resistance to gemcitabine via activation of ERK1/2. FN-blocking agents added to gemcitabine-based chemotherapy might counteract chemoresistance in PDAC and provide better clinical outcomes.
Keywords: Chemoresistance; Extracellular matrix; Fibronectin; Gemcitabine; Pancreatic cancer; Pancreatic stellate cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Paracrine HGF promotes EMT and mediates the effects of PSC on chemoresistance by activating c-Met/PI3K/Akt signaling in pancreatic cancer in vitro.Life Sci. 2020 Dec 15;263:118523. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118523. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 33039386
-
Pancreatic stellate cell-induced gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer is associated with LDHA- and MCT4-mediated enhanced glycolysis.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Jan 19;23(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02852-7. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 36658582 Free PMC article.
-
Paracrine SDF-1α signaling mediates the effects of PSCs on GEM chemoresistance through an IL-6 autocrine loop in pancreatic cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Feb 20;6(5):3085-97. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3099. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25609203 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrotic Fortresses and Therapeutic Frontiers: Pancreatic Stellate Cells and the Extracellular Matrix in Pancreatic Cancer.Cancer Med. 2025 Jun;14(11):e70788. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70788. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40437741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting apoptosis pathways in pancreatic cancer.Cancer Lett. 2013 May 28;332(2):346-58. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.10.015. Epub 2010 Nov 13. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 21078544 Review.
Cited by
-
Research advances of secretory proteins in malignant tumors.Chin J Cancer Res. 2021 Feb 28;33(1):115-132. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2021.01.12. Chin J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33707934 Free PMC article.
-
Three-Dimensional Cell Culture Systems in Radiopharmaceutical Cancer Research.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 25;12(10):2765. doi: 10.3390/cancers12102765. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32993034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Genetic Alterations to Tumor Microenvironment: The Ariadne's String in Pancreatic Cancer.Cells. 2020 Jan 28;9(2):309. doi: 10.3390/cells9020309. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32012917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicine Strategies for Targeting Tumor Stroma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 17;15(16):4145. doi: 10.3390/cancers15164145. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The glutathione S-transferase Gstt1 drives survival and dissemination in metastases.Nat Cell Biol. 2024 Jun;26(6):975-990. doi: 10.1038/s41556-024-01426-7. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Nat Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38862786
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

