Minichromosome maintenance 3 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma radioresistance by activating the NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 31208444
- PMCID: PMC6580494
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-019-1241-9
Minichromosome maintenance 3 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma radioresistance by activating the NF-κB pathway
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Minichromosome maintenance 3 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma radioresistance by activating the NF-κB pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Aug 2;38(1):336. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1338-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31375140 Free PMC article.
-
Correction to: Minichromosome maintenance 3 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma radioresistance by activating the NF-κB pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Sep 5;38(1):387. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1395-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31488195 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common tumors in the worldwide, it develops resistance to radiotherapy during treatment, understanding the regulatory mechanisms of radioresistance generation is the urgent need for HCC therapy.
Methods: qRT-PCR, western blot and immunohistochemistry were used to examine MCM3 expression. MTT assay, colony formation assay, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase nick end labeling assay and In vivo xenograft assay were used to determine the effect of MCM3 on radioresistance. Gene set enrichment analysis, luciferase reporter assay, western blot and qRT-PCR were used to examine the effect of MCM3 on NF-κB pathway.
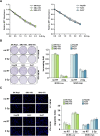
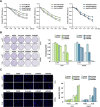
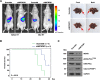
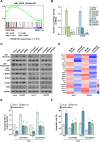
Results: We found DNA replication initiation protein Minichromosome Maintenance 3 (MCM3) was upregulated in HCC tissues and cells, patients with high MCM3 expression had poor outcome, it was an independent prognostic factor for HCC. Cells with high MCM3 expression or MCM3 overexpression increased the radioresistance determined by MTT assay, colony formation assay, TUNEL assay and orthotopic transplantation mouse model, while cells with low MCM3 expression or MCM3 knockdown reduced the radioresistance. Mechanism analysis showed MCM3 activated NF-κB pathway, characterized by increasing the nuclear translocation of p65, the expression of the downstream genes NF-κB pathway and the phosphorylation of IKK-β and IκBα. Inhibition of NF-κB in MCM3 overexpressing cells using small molecular inhibitor reduced the radioresistance, suggesting MCM3 increased radioresistance through activating NF-κB pathway. Moreover, we found MCM3 expression positively correlated with NF-κB pathway in clinic.
Conclusions: Our findings revealed that MCM3 promoted radioresistance through activating NF-κB pathway, strengthening the role of MCM subunits in the tumor progression and providing a new target for HCC therapy.
Keywords: HCC; MCM3; NF-κB pathway; Radiotherapy resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Aurora-a confers radioresistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma by activating NF-κB signaling pathway.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 8;19(1):1075. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6312-y. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31703572 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor α-induced protein 1 as a novel tumor suppressor through selective downregulation of CSNK2B blocks nuclear factor-κB activation in hepatocellular carcinoma.EBioMedicine. 2020 Jan;51:102603. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.102603. Epub 2020 Jan 3. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 31901862 Free PMC article.
-
MCM3 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition through AKT/Twist signaling pathway.Ann Hepatol. 2025 Jan-Jun;30(1):101785. doi: 10.1016/j.aohep.2025.101785. Epub 2025 Feb 18. Ann Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 39978465
-
Multifaceted role of NF-κB in hepatocellular carcinoma therapy: Molecular landscape, therapeutic compounds and nanomaterial approaches.Environ Res. 2023 Jul 1;228:115767. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.115767. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 36966991 Review.
-
Radioresistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Biological Bases and Therapeutic Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 21;26(5):1839. doi: 10.3390/ijms26051839. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076465 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bioinformatics-based identification of miRNAs, mRNA, and regulatory signaling pathways involved in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2022 Summer;15(3):232-240. doi: 10.22037/ghfbb.v15i3.2465. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2022. PMID: 36311956 Free PMC article.
-
Role of tight junction-associated MARVEL protein marvelD3 in migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Adh Migr. 2021 Dec;15(1):249-260. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2021.1958441. Cell Adh Migr. 2021. PMID: 34338154 Free PMC article.
-
Osthole inhibits GSK-3β/AMPK/mTOR pathway-controlled glycolysis and increases radiosensitivity of subcutaneous transplanted hepatocellular carcinoma in nude mice.Strahlenther Onkol. 2024 May;200(5):444-452. doi: 10.1007/s00066-023-02173-8. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Strahlenther Onkol. 2024. PMID: 37963994
-
Screening prognostic markers for hepatocellular carcinoma based on pyroptosis-related lncRNA pairs.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 Apr 29;24(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05299-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 37120506 Free PMC article.
-
Copper in Cancer: from transition metal to potential target.Hum Cell. 2024 Jan;37(1):85-100. doi: 10.1007/s13577-023-00985-5. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Hum Cell. 2024. PMID: 37751026 Review.
References
-
- Lachenmayer A, Alsinet C, Savic R, Cabellos L, Toffanin S, Hoshida Y, Villanueva A, Minguez B, Newell P, Tsai HW, et al. Wnt-pathway activation in two molecular classes of hepatocellular carcinoma and experimental modulation by sorafenib. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(18):4997–5007. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2322. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81602701/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81760496/the Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2016A030313195/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2014A030313131/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2017A030313547/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2018A030313176/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2014B020228003/Key Scientific and Technological Projects of Guangdong Province
- 2015A070710006/Key Scientific and Technological Projects of Guangdong Province
- 2016A020215053/Key Scientific and Technological Projects of Guangdong Province
- 2014B030301041/Key Scientific and Technological Projects of Guangdong Province
- 201400000001-3/Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou
- 158100076/Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou
- 201507020037/Ministry of Science and Technology (VN)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

