An appraisal of natural products active against parasitic nematodes of animals
- PMID: 31208455
- PMCID: PMC6580475
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-019-3537-1
An appraisal of natural products active against parasitic nematodes of animals
Abstract
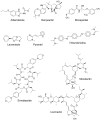
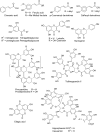
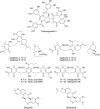
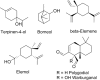
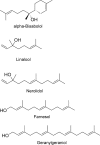
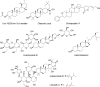
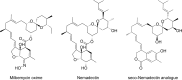
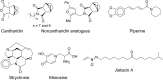
Here, the scientific and patent literature on the activities of purified natural compounds has been reviewed, with the aim of assessing their suitability as anthelmintic drug discovery starting points. Only compounds described as active against parasitic nematodes of animals or against the model nematode Caenorhabditis elegans have been analysed. Scientific articles published since 2010 and patents granted from 2000, both inclusive, have been included in this analysis. The results show a scarcity of novel chemical structures, a limited follow-up of compounds disclosed before 2010 and a bias towards the screening of plant products, almost to the exclusion of other sources, when microbial extracts have, historically, provided most starting points for anti-infective drugs. All plant products published in this period were previously known, alerting to the high re-discovery rates of a limited number of chemical classes from this source. The most promising compounds described in the literature reviewed here, namely the linear nemadectin-derivatives, are novel and of bacterial origin. Patented but otherwise unpublished spiroketal structures also appear as interesting scaffolds for future development. The patent literature confirmed that it is possible to patent derivatives of previously known products, making them valid starting points for translational research.
Keywords: Animals; Anthelmintics; Natural products; Nematocides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
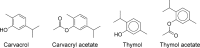
Similar articles
-
Plant-Based Natural Products for the Discovery and Development of Novel Anthelmintics against Nematodes.Biomolecules. 2020 Mar 9;10(3):426. doi: 10.3390/biom10030426. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32182910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A perspective on the discovery of selected compounds with anthelmintic activity against the barber's pole worm-Where to from here?Adv Parasitol. 2020;108:1-45. doi: 10.1016/bs.apar.2019.12.003. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Adv Parasitol. 2020. PMID: 32291083 Review.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans as a model to screen plant extracts and compounds as natural anthelmintics for veterinary use.Vet Parasitol. 2011 Dec 15;182(2-4):264-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.05.020. Epub 2011 May 24. Vet Parasitol. 2011. PMID: 21680095
-
Screening of the 'Open Scaffolds' collection from Compounds Australia identifies a new chemical entity with anthelmintic activities against different developmental stages of the barber's pole worm and other parasitic nematodes.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2017 Dec;7(3):286-294. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2017.05.004. Epub 2017 May 28. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2017. PMID: 28732272 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the discovery and development of anthelmintics by harnessing natural product scaffolds.Adv Parasitol. 2021;111:203-251. doi: 10.1016/bs.apar.2020.10.002. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Adv Parasitol. 2021. PMID: 33482975 Review.
Cited by
-
Anthelmintic Effect of Cannabidiol against Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2024 Jan 31;9(2):35. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed9020035. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38393124 Free PMC article.
-
An Inventory of Anthelmintic Plants across the Globe.Pathogens. 2023 Jan 13;12(1):131. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12010131. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 36678480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of 2-undecanol produced by Paenibacillus polymyxa KM2501-1 in controlling Meloidogyne incognita.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Aug 5;13(8):e0306224. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03062-24. Epub 2025 Jun 26. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40569064 Free PMC article.
-
Antihelminthic Activity of Lophira Lanceolata on Heligmosomoides polygyrus Using an Automated High-Throughput Method.J Trop Med. 2023 Jan 20;2023:9504296. doi: 10.1155/2023/9504296. eCollection 2023. J Trop Med. 2023. PMID: 36713298 Free PMC article.
-
Oscillatoria sp. as a Potent Anti-phytopathogenic Agent and Plant Immune Stimulator Against Root-Knot Nematode of Soybean cv. Giza 111.Front Plant Sci. 2022 May 26;13:870518. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.870518. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35720553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson RC. Nematode parasites of vertebrates. Their development and transmission. 2. Wallingford: CABI Publishing; 2000.
-
- WHO. Soil-transmitted Helminth Infections. 2018. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/soil-transmitted-helmin.... Accessed 12 Dec 2018.
-
- WHO. Global health estimates 2016: disease burden by cause, age, sex, by country and by region, 2000–2016. In: Global Health Estimates. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

