Effect of biomimetic mineralization on enamel and dentin: A Raman and EDX analysis
- PMID: 31208774
- PMCID: PMC9668404
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dental.2019.05.025
Effect of biomimetic mineralization on enamel and dentin: A Raman and EDX analysis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of an experimental biomimetic mineralization kit (BIMIN) on the chemical composition and crystallinity of caries-free enamel and dentin samples in vitro.
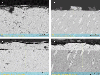
Methods: Enamel and dentin samples from 20 human teeth (10 for enamel; 10 for dentin) were divided into a control group without treatment and test samples with BIMIN treatment. Quantitative analysis of tissue penetration of fluoride, phosphate, and calcium was performed using energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). Mineralization depth was measured by Raman spectroscopy probing the symmetric valence vibration near 960cm-1 as a marker for crystallinity. EDX data was statistically analyzed using a paired t-test and Raman data was analyzed using the Student's t-test.
Results: EDX analysis demonstrated a penetration depth of fluoride of 4.10±3.32μm in enamel and 4.31±2.67μm in dentin. Calcium infiltrated into enamel 2.65±0.64μm and into dentin 5.58±1.63μm, while the penetration depths for phosphate were 4.83±2.81μm for enamel and 6.75±3.25μm for dentin. Further, up to 25μm of a newly mineralized enamel-like layer was observed on the surface of the samples. Raman concentration curves demonstrated an increased degree of mineralization up to 5-10μm into the dentin and enamel samples.
Significance: Biomimetic mineralization of enamel and dentin samples resulted in an increase of mineralization and a penetration of fluoride into enamel and dentin.
Keywords: Biomimetic; Dentin; EDX; Enamel; Mineralization; Raman.
Copyright © 2019 The Academy of Dental Materials. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare to have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Amelogenin-inspired peptide, calcium phosphate solution, fluoride and their synergistic effect on enamel biomimetic remineralization: an in vitro pH-cycling model.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Feb 27;24(1):279. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04008-z. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38413983 Free PMC article.
-
Biomimetic transformation of polyphosphate microparticles during restoration of damaged teeth.Dent Mater. 2019 Feb;35(2):244-256. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2018.11.014. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Dent Mater. 2019. PMID: 30522697
-
Remineralization of Artificially Demineralized Human Enamel and Dentin Samples by Zinc-Carbonate Hydroxyapatite Nanocrystals.Materials (Basel). 2022 Oct 14;15(20):7173. doi: 10.3390/ma15207173. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36295240 Free PMC article.
-
Biomineralization during early stages of the developing tooth in vitro with special reference to secretory stage of amelogenesis.Int J Dev Biol. 1995 Feb;39(1):203-12. Int J Dev Biol. 1995. PMID: 7626408 Review.
-
[Factors that modify de- and remineralization in dental enamel from the aspect of caries susceptibility].Ann Acad Med Stetin. 1999;Suppl 47:1-89. Ann Acad Med Stetin. 1999. PMID: 10462837 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Biomimetic Tissue Engineering Strategies for Craniofacial Applications.Biomimetics (Basel). 2024 Oct 18;9(10):636. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics9100636. Biomimetics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Modern Multidisciplinary Method to Characterize Natural White Spot Lesions with 2D and 3D Assessments: A Preliminary Study.J Pers Med. 2024 May 19;14(5):542. doi: 10.3390/jpm14050542. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38793124 Free PMC article.
-
Elemental Compositions of Enamel or Dentin in Human and Bovine Teeth Differ from Murine Teeth.Materials (Basel). 2023 Feb 11;16(4):1514. doi: 10.3390/ma16041514. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36837152 Free PMC article.
-
Physicochemical understanding of biomineralization by molecular vibrational spectroscopy: From mechanism to nature.Exploration (Beijing). 2023 Jul 26;3(6):20230033. doi: 10.1002/EXP.20230033. eCollection 2023 Dec. Exploration (Beijing). 2023. PMID: 38264681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morpho-Chemical Observations of Human Deciduous Teeth Enamel in Response to Biomimetic Toothpastes Treatment.Materials (Basel). 2020 Apr 11;13(8):1803. doi: 10.3390/ma13081803. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32290403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartlett DW, Lussi A, West NX, Bouchard P, Sanz M, Bourgeois D. Prevalence of tooth wear on buccal and lingual surfaces and possible risk factors in young European adults. J Dent. 2013;41:1007–13. - PubMed
-
- Staines M, Robinson W, Hood J. Spherical indentation of tooth enamel. Journal of materials science. 1981;16:2551–6.
-
- Nanci A Ten cate’s oral histology-pageburst on vitalsource: development, structure, and function: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

