Validation of NEDD8-conjugating enzyme UBC12 as a new therapeutic target in lung cancer
- PMID: 31208947
- PMCID: PMC6642072
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.06.005
Validation of NEDD8-conjugating enzyme UBC12 as a new therapeutic target in lung cancer
Abstract
Background: The neddylation pathway is overactivated in human cancers. Inhibition of neddylation pathway has emerged as an attractive anticancer strategy. The mechanisms underlying neddylation overactivation in cancer remain elusive. MLN4924/Pevonedistat, a first-in-class NEDD8-activating enzyme (NAE, E1) inhibitor, exerts significant anti-tumor effects, but its mutagenic resistance remains unresolved.
Methods: The expression of NEDD8-conjugating enzyme UBC12/UBE2M (E2) and NEDD8 were estimated by bioinformatics analysis and western blot in human lung cancer cell lines. The malignant phenotypes of lung cancer cells were evaluated both in vitro and in vivo upon UBC12 knockdown. Cell-cycle arrest was evaluated by quantitative proteomic analysis and propidium iodide stain and fluorescence - activated cell sorting (FACS). The growth of MLN4924 - resistant H1299 cells was also evaluated upon UBC12 knockdown.
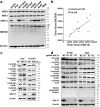
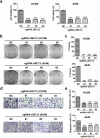
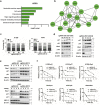
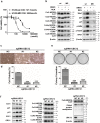
Findings: The mRNA level of UBC12 in lung cancer tissues was much higher than that in normal lung tissues, increased with disease deterioration, and positively correlated with NEDD8 expression. Moreover, the overexpression of UBC12 significantly enhanced protein neddylation modification whereas the downregulation of UBC12 reduced neddylation modification of target proteins. Functionally, neddylation inactivation by UBC12 knockdown suppressed the malignant phenotypes of lung cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. The quantitative proteomic analysis and cell cycle profiling showed that UBC12 knockdown disturbed cell cycle progression by triggering G2 phase cell-cycle arrest. Further mechanistical studies revealed that UBC12 knockdown inhibited Cullin neddylation, led to the inactivation of CRL E3 ligases and induced the accumulation of tumor-suppressive CRL substrates (p21, p27 and Wee1) to induce cell cycle arrest and suppress the malignant phenotypes of lung cancer cells. Finally, UBC12 knockdown effectively inhibited the growth of MLN4924-resistant lung cancer cells.
Interpretation: These findings highlight a crucial role of UBC12 in fine-tuned regulation of neddylation activation status and validate UBC12 as an attractive alternative anticancer target against neddylation pathway. FUND: Chinese Minister of Science and Technology grant (2016YFA0501800), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81401893, 81625018, 81820108022, 81772470, 81572340 and 81602072), Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (2019-01-07-00-10-E00056), Program of Shanghai Academic/Technology Research Leader (18XD1403800), National Thirteenth Five-Year Science and Technology Major Special Project for New Drug and Development (2017ZX09304001). The funders had no role in study design, data collection, data analysis, interpretation, writing of the report.
Keywords: Anticancer target; Cell-cycle arrest; Lung cancer; Overcome drug resistance; UBC12.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Targeting neddylation E2 for anticancer therapy, putting new wine into new bottles?EBioMedicine. 2019 Jul;45:3-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.07.012. Epub 2019 Jul 9. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31300349 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Overactivated neddylation pathway as a therapeutic target in lung cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014 May 22;106(6):dju083. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju083. Print 2014 Jun. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014. PMID: 24853380
-
Suppression of glioblastoma by targeting the overactivated protein neddylation pathway.Neuro Oncol. 2015 Oct;17(10):1333-43. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov066. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Neuro Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25904638 Free PMC article.
-
A first-in-class inhibitor, MLN4924 (pevonedistat), induces cell-cycle arrest, senescence, and apoptosis in human renal cell carcinoma by suppressing UBE2M-dependent neddylation modification.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018 Jun;81(6):1083-1093. doi: 10.1007/s00280-018-3582-z. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29667067
-
Targeting DCN1-UBC12 Protein-Protein Interaction for Regulation of Neddylation Pathway.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1217:349-362. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-1025-0_20. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31898237 Review.
-
Targeting Neddylation pathways to inactivate cullin-RING ligases for anticancer therapy.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Dec 10;21(17):2383-400. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5795. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24410571 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting NEDD8 suppresses surgical stress-facilitated metastasis of colon cancer via restraining regulatory T cells.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jan 5;15(1):8. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06396-6. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38177106 Free PMC article.
-
Neddylation activated TRIM25 desensitizes triple-negative breast cancer to paclitaxel via TFEB-mediated autophagy.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 26;43(1):177. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03085-w. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38926803 Free PMC article.
-
Function, mechanism and drug discovery of ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like modification with multiomics profiling for cancer therapy.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 Nov;13(11):4341-4372. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.019. Epub 2023 Jul 22. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 37969742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NNMT/1-MNA Promote Cell-Cycle Progression of Breast Cancer by Targeting UBC12/Cullin-1-Mediated Degradation of P27 Proteins.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Mar;11(9):e2305907. doi: 10.1002/advs.202305907. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38126621 Free PMC article.
-
The CRL3BTBD9 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex targets TNFAIP1 for degradation to suppress cancer cell migration.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Apr 24;5(1):42. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0140-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32327643 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

