Is high-sensitivity troponin, alone or in combination with copeptin, sensitive enough for ruling out NSTEMI in very early presenters at admission? A post hoc analysis performed in emergency departments
- PMID: 31209082
- PMCID: PMC6589015
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-023994
Is high-sensitivity troponin, alone or in combination with copeptin, sensitive enough for ruling out NSTEMI in very early presenters at admission? A post hoc analysis performed in emergency departments
Abstract
Objectives: Copeptin and high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (HS-cTn) assays improve the early detection of non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI). Their sensitivities may, however, be reduced in very early presenters.
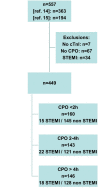
Setting: We performed a post hoc analysis of three prospective studies that included patients who presented to the emergency department for chest pain onset (CPO) of less than 6 hours.
Participants: 449 patients were included, in whom 12% had NSTEMI. CPO occurred <2 hours from ED presentation in 160, between 2 and 4 hours in 143 and >4 hours in 146 patients. The prevalence of NSTEMI was similar in all groups (9%, 13% and 12%, respectively, p=0.281).
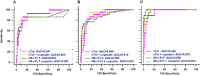
Measures: Diagnostic performances of HS-cTn and copeptin at presentation were examined according to CPO. The discharge diagnosis was adjudicated by two experts, including cardiac troponin I (cTnI). HS-cTn and copeptin were blindly measured.
Results: Diagnostic accuracies of cTnI, cTnI +copeptin and HS-cardiac troponin T (HS-cTnT) (but not HS-cTnT +copeptin) lower through CPO categories. For patients with CPO <2 hours, the choice of a threshold value of 14 ng/L for HS-cTnT resulted in three false negative (Sensitivity 80%(95% CI 51% to 95%); specificity 85% (95% CI 78% to 90%); 79% of correctly ruled out patients) and that of 5 ng/L in two false negative (sensitivity 87% (95% CI 59% to 98%); specificity 58% (95% CI 50% to 66%); 52% of correctly ruled out patients). The addition of copeptin to HS-cTnT induced a decrease of misclassified patients to 1 in patients with CPO <2 hours (sensitivity 93% (95% CI 66% to 100%); specificity 41% (95% CI 33% to 50%)).
Conclusion: A single measurement of HS-cTn, alone or in combination with copeptin at admission, seems not safe enough for ruling out NSTEMI in very early presenters (with CPO <2 hours).
Trial registration number: DC-2009-1052.
Keywords: chest pain; chest pain onset; copeptin; high sensitive cardiac troponin; non st-elevation acute myocardial infarction; very early presenters.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: CC-G, PR and CM received honorarias and lecture fees from Roche Diagnostics andThermofisher Scientific.
Figures
References
-
- Roffi M, Patrono C, Collet JP, et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation: Task Force for the Management of Acute Coronary Syndromes in Patients Presenting without Persistent ST-Segment Elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 20162016;37:267–315. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
