Structural and biochemical characterization of 20β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Bifidobacterium adolescentis strain L2-32
- PMID: 31209107
- PMCID: PMC6690682
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009390
Structural and biochemical characterization of 20β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Bifidobacterium adolescentis strain L2-32
Abstract
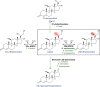
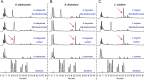
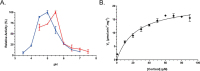
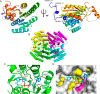
Anaerobic bacteria inhabiting the human gastrointestinal tract have evolved various enzymes that modify host-derived steroids. The bacterial steroid-17,20-desmolase pathway cleaves the cortisol side chain, forming pro-androgens predicted to impact host physiology. Bacterial 20β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (20β-HSDH) regulates cortisol side-chain cleavage by reducing the C-20 carboxyl group on cortisol, yielding 20β-dihydrocortisol. Recently, the gene encoding 20β-HSDH in Butyricicoccus desmolans ATCC 43058 was reported, and a nonredundant protein search yielded a candidate 20β-HSDH gene in Bifidobacterium adolescentis strain L2-32. B. adolescentis 20β-HSDH could regulate cortisol side-chain cleavage by limiting pro-androgen formation in bacteria such as Clostridium scindens and 21-dehydroxylation by Eggerthella lenta Here, the putative B. adolescentis 20β-HSDH was cloned, overexpressed, and purified. 20β-HSDH activity was confirmed through whole-cell and pure enzymatic assays, and it is specific for cortisol. Next, we solved the structures of recombinant 20β-HSDH in both the apo- and holo-forms at 2.0-2.2 Å resolutions, revealing close overlap except for rearrangements near the active site. Interestingly, the structures contain a large, flexible N-terminal region that was investigated by gel-filtration chromatography and CD spectroscopy. This extended N terminus is important for protein stability because deletions of varying lengths caused structural changes and reduced enzymatic activity. A nonconserved extended N terminus was also observed in several short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase family members. B. adolescentis strains capable of 20β-HSDH activity could alter glucocorticoid metabolism in the gut and thereby serve as potential probiotics for the management of androgen-dependent diseases.
Keywords: 20β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; Bifidobacteria; C-20 reduction; Steroid-17,20-desmolase; androgen; cortisol; glucocorticoid; microbiome; oxidation–reduction (redox); probiotic.
© 2019 Doden et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of a 20β-HSDH from the anaerobic gut bacterium Butyricicoccus desmolans ATCC 43058.J Lipid Res. 2017 May;58(5):916-925. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M074914. Epub 2017 Mar 17. J Lipid Res. 2017. PMID: 28314858 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism of Oxo-Bile Acids and Characterization of Recombinant 12α-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenases from Bile Acid 7α-Dehydroxylating Human Gut Bacteria.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 May 1;84(10):e00235-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00235-18. Print 2018 May 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29549099 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Synthesis and Characterization of a Gene Cluster Encoding NAD(P)H-Dependent 3α-, 3β-, and 12α-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenases from Eggerthella CAG:298, a Gut Metagenomic Sequence.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Mar 19;84(7):e02475-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02475-17. Print 2018 Apr 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29330189 Free PMC article.
-
Gut feelings about bacterial steroid-17,20-desmolase.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021 Apr 5;525:111174. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2021.111174. Epub 2021 Jan 24. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 33503463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-function relationships in 3alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases: a comparison of the rat and human isoforms.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2003 Jun;85(2-5):247-55. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(03)00236-x. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12943710 Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial steroid-17,20-desmolase is a taxonomically rare enzymatic pathway that converts prednisone to 1,4-androstanediene-3,11,17-trione, a metabolite that causes proliferation of prostate cancer cells.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2020 May;199:105567. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.105567. Epub 2019 Dec 20. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31870912 Free PMC article.
-
The Androbactome and the Gut Microbiota-Testis Axis: A Narrative Review of Emerging Insights into Male Fertility.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 27;26(13):6211. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136211. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating androgen regulation by androgen-catabolizing gut bacteria in male mouse gut.Gut Microbes. 2023 Jan-Dec;15(1):2183685. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2183685. Gut Microbes. 2023. PMID: 36843073 Free PMC article.
-
The potential influence and intervention measures of gut microbiota on sperm: it is time to focus on testis-gut microbiota axis.Front Microbiol. 2024 Oct 8;15:1478082. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1478082. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39439945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clostridium scindens: history and current outlook for a keystone species in the mammalian gut involved in bile acid and steroid metabolism.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2025 Jan 14;49:fuaf016. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuaf016. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2025. PMID: 40307670 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ridlon J. M., Ikegawa S., Alves J. M., Zhou B., Kobayashi A., Iida T., Mitamura K., Tanabe G., Serrano M., De Guzman A., Cooper P., Buck G. A., and Hylemon P. B. (2013) Clostridium scindens: a human gut microbe with a high potential to convert glucocorticoids into androgens. J. Lipid Res. 54, 2437–2449 10.1194/jlr.M038869 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mythen S. M., Devendran S., Méndez-García C., Cann I., and Ridlon J. M. (2018) Targeted synthesis and characterization of a gene cluster encoding NAD(P)H-dependent 3α-, 3β-, and 12α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases from Eggerthella CAG:298, a gut metagenomic sequence. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 84, e02475–17 10.1128/AEM.02475-17 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

