Contribution of hla Regulation by SaeR to Staphylococcus aureus USA300 Pathogenesis
- PMID: 31209148
- PMCID: PMC6704604
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00231-19
Contribution of hla Regulation by SaeR to Staphylococcus aureus USA300 Pathogenesis
Abstract
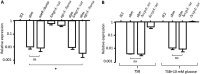
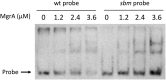
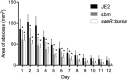
The SaeRS two-component system in Staphylococcus aureus is critical for regulation of many virulence genes, including hla, which encodes alpha-toxin. However, the impact of regulation of alpha-toxin by Sae on S. aureus pathogenesis has not been directly addressed. Here, we mutated the SaeR-binding sequences in the hla regulatory region and determined the contribution of this mutation to hla expression and pathogenesis in strain USA300 JE2. Western blot analyses revealed drastic reduction of alpha-toxin levels in the culture supernatants of SaeR-binding mutant in contrast to the marked alpha-toxin production in the wild type. The SaeR-binding mutation had no significant effect on alpha-toxin regulation by Agr, MgrA, and CcpA. In animal studies, we found that the SaeR-binding mutation did not contribute to USA300 JE2 pathogenesis using a rat infective endocarditis model. However, in a rat skin and soft tissue infection model, the abscesses on rats infected with the mutant were significantly smaller than the abscesses on those infected with the wild type but similar to the abscesses on those infected with a saeR mutant. These studies indicated that there is a direct effect of hla regulation by SaeR on pathogenesis but that the effect depends on the animal model used.
Keywords: Sae; Staphylococcus aureus; alpha-toxin; virulence regulation.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MgrA activates expression of capsule genes, but not the α-toxin gene in experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis.J Infect Dis. 2013 Dec 1;208(11):1841-8. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit367. Epub 2013 Jul 30. J Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23901087 Free PMC article.
-
The SaeRS Two-Component System Is a Direct and Dominant Transcriptional Activator of Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin 1 in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2016 Sep 9;198(19):2732-42. doi: 10.1128/JB.00425-16. Print 2016 Oct 1. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27457715 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the regulatory loci agr, sarA and sae of Staphylococcus aureus on the induction of alpha-toxin during device-related infection resolved by direct quantitative transcript analysis.Mol Microbiol. 2001 Jun;40(6):1439-47. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02494.x. Mol Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11442841
-
Nutritional Regulation of the Sae Two-Component System by CodY in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2018 Mar 26;200(8):e00012-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00012-18. Print 2018 Apr 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29378891 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the Sae Two-Component System by Branched-Chain Fatty Acids in Staphylococcus aureus.mBio. 2022 Oct 26;13(5):e0147222. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01472-22. Epub 2022 Sep 22. mBio. 2022. PMID: 36135382 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of an antivirulence agent targeting the master regulator of virulence genes in Staphylococcus aureus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Oct 31;13:1268044. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1268044. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38029271 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of α-hemolysin activity of Staphylococcus aureus by theaflavin 3,3'-digallate.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 31;18(8):e0290904. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290904. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37651426 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiofilm Activities of Multiple Halogenated Pyrimidines Against Staphylococcus aureus.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 28;25(23):12830. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312830. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684543 Free PMC article.
-
Sub-inhibitory concentrations of tigecycline could attenuate the virulence of Staphylococcus aureus by inhibiting the product of α-toxin.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Mar 19;13(5):e0134424. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01344-24. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40105354 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the Staphylococcus aureus intramembrane sensing histidine kinase SaeS via intramembrane interaction with the bacterially encoded small protein ScrA.mBio. 2025 Jul 9;16(7):e0153125. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01531-25. Epub 2025 Jun 20. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40539774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tuchscherr L, Bischoff M, Lattar SM, Noto Llana M, Pförtner H, Niemann S, Geraci J, Van de Vyver H, Fraunholz MJ, Cheung AL, Herrmann M, Völker U, Sordelli DO, Peters G, Löffler B. 2015. Sigma factor SigB is crucial to mediate Staphylococcus aureus adaptation during chronic infections. PLoS Pathog 11:e1004870. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004870. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boisset S, Geissmann T, Huntzinger E, Fechter P, Bendridi N, Possedko M, Chevalier C, Helfer AC, Benito Y, Jacquier A, Gaspin C, Vandenesch F, Romby P. 2007. Staphylococcus aureus RNAIII coordinately represses the synthesis of virulence factors and the transcription regulator Rot by an antisense mechanism. Genes Dev 21:1353–1366. doi:10.1101/gad.423507. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

