Characterization of intellectual disability and autism comorbidity through gene panel sequencing
- PMID: 31209962
- PMCID: PMC7428836
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.23822
Characterization of intellectual disability and autism comorbidity through gene panel sequencing
Erratum in
-
Characterization of intellectual disability and autism comorbidity through gene panel sequencing.Hum Mutat. 2020 Jun;41(6):1183. doi: 10.1002/humu.24012. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Hum Mutat. 2020. PMID: 32400065 No abstract available.
Abstract
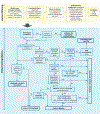
Intellectual disability (ID) and autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are clinically and genetically heterogeneous diseases. Recent whole exome sequencing studies indicated that genes associated with different neurological diseases are shared across disorders and converge on common functional pathways. Using the Ion Torrent platform, we developed a low-cost next-generation sequencing gene panel that has been transferred into clinical practice, replacing single disease-gene analyses for the early diagnosis of individuals with ID/ASD. The gene panel was designed using an innovative in silico approach based on disease networks and mining data from public resources to score disease-gene associations. We analyzed 150 unrelated individuals with ID and/or ASD and a confident diagnosis has been reached in 26 cases (17%). Likely pathogenic mutations have been identified in another 15 patients, reaching a total diagnostic yield of 27%. Our data also support the pathogenic role of genes recently proposed to be involved in ASD. Although many of the identified variants need further investigation to be considered disease-causing, our results indicate the efficiency of the targeted gene panel on the identification of novel and rare variants in patients with ID and ASD.
Keywords: ASD; ID; NGS; comorbidity; gene panel; variant interpretation.
© 2019 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abdelmoity AT, LePichon J-B, Nyp SS, Soden SE, Daniel CA, Yu S. 2012. 15q11.2 proximal imbalances associated with a diverse array of neuropsychiatric disorders and mild dysmorphic features. J Dev Behav Pediatr 33:570–576. - PubMed
-
- Almuhtaseb S, Oppewal A, Hilgenkamp TIM. 2014. Gait characteristics in individuals with intellectual disabilities: a literature review. Res Dev Disabil 35:2858–2883. - PubMed

