LncRNA FOXD2-AS1 as a competitive endogenous RNA against miR-150-5p reverses resistance to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 31210410
- PMCID: PMC6714507
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14465
LncRNA FOXD2-AS1 as a competitive endogenous RNA against miR-150-5p reverses resistance to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
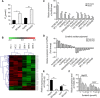
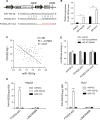
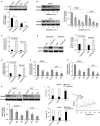
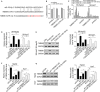
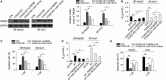
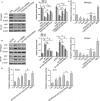
The current study elucidated the role of a long non-coding RNA (lncRNA), FOXD2-AS1, in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and the regulatory mechanism underlying FOXD2-AS1/miR-150-5p/transmembrane protein 9 (TMEM9) signalling in HCC. Microarray analysis was used for preliminary screening of candidate lncRNAs in HCC tissues. qRT-PCR and Western blot analyses were used to detect the expression of FOXD2-AS1. Cell proliferation assays, luciferase assay and RNA immunoprecipitation were performed to examine the mechanism by which FOXD2-AS1 mediates sorafenib resistance in HCC cells. FOXD2-AS1 and TMEM9 were significantly decreased and miR-150-5p was increased in SR-HepG2 and SR-HUH7 cells compared with control parental cells. Overexpression of FOXD2-AS1 increased TMEM9 expression and overcame the resistance of SR-HepG2 and SR-HUH7 cells. Conversely, knockdown of FOXD2-AS1 decreased TMEM9 expression and increased the sensitivity of HepG2 and Huh7 cells to sorafenib. Our data also demonstrated that FOXD2-AS1 functioned as a sponge for miR-150-5p to modulate TMEM9 expression. Taken together, our findings revealed that FOXD2-AS1 is an important regulator of TMEM9 and contributed to sorafenib resistance. Thus, FOXD2-AS1 may serve as a therapeutic target against sorafenib resistance in HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); long non-coding RNA (lncRNA); pathogenesis; proliferation; resistance; sorafenib.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ng KT, Lo CM, Guo DY, et al. Identification of transmembrane protein 98 as a novel chemoresistance‐conferring gene in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13:1285‐1297. - PubMed
-
- Deng Y, Du Y, Zhang Q, Han X, Cao G. Human cytidine deaminases facilitate hepatitis B virus evolution and link inflammation and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2014;343:161‐171. - PubMed
-
- Yu C, Wang Z, Xu X, Xiang W, Huang X. Circulating hepatocellular carcinoma cells are characterized by CXCR4 and MMP26. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36:2393‐2402. - PubMed
-
- Zhu H, Zhou X, Ma C, et al. Low expression of miR‐448 induces EMT and promotes invasion by regulating ROCK2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36:487‐498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

