Expression fusion immunogen by live attenuated Escherichia coli against enterotoxins infection in mice
- PMID: 31210426
- PMCID: PMC6680629
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.13447
Expression fusion immunogen by live attenuated Escherichia coli against enterotoxins infection in mice
Abstract
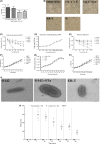
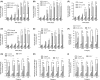
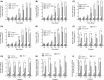
Previous epidemiological studies have shown that enterotoxins from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) appear to be the most important causes of neonatal piglet and porcine post-weaning diarrhoea (PWD). Thus, it is necessary to develop an effective vaccine against ETEC infection. In the present study, the Kil cassette was inserted into the pseudogene yaiT by homologous recombination to create an attenuated E. coli double selection platform O142(yaiT-Kil). After that, PRPL-Kil was replaced with a fusion gene (LTA1-STa13 -STb-LTA2-LTB-STa13 -STb) to establish oral vaccines O142(yaiT::LTA1-STa13 -STb-LTA2-LTB-STa13 -STb) (ER-T). Subsequently, BALB/c mice were orally immunized with ER-T. Results showed that serum IgG and faecal sIgA responded against all ETEC enterotoxins and induced F41 antibody in BALB/c mice by orogastrically inoculation with recombinant E. coli ER-T. Moreover, the determination of cellular immune response demonstrated that the stimulation index (SI) was significantly higher in immunized mice than in control mice, and a clear trend in the helper T-cell (Th) response was Th2-cell (IL-4) exceed Th1-cell (IFN-γ).Our results indicated that recombinant E. coli ER-T provides effective protection against ETEC infection.
© 2019 The Authors. Microbial Biotechnology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Society for Applied Microbiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures






References
-
- Balakirev, E.S. , and Ayala, F.J. (2003) Pseudogenes: are they “junk” or functional DNA? Annu Rev Genet 37: 123–151. - PubMed
-
- Blanco, M. , Blanco, J.E. , Gonzalez, E.A. , Mora, A. , Jansen, W. , Gomes, T.A. , et al (1997) Genes coding for enterotoxins and verotoxins in porcine Escherichia coli strains belonging to different O:K: H serotypes: relationship with toxic phenotypes. J Clin Microbiol 35: 2958–2963. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Charles, I. , and Dougan, G. (1990) Gene expression and the development of live enteric vaccines. Trends Biotechnol 8: 117–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

