Melatonin Attenuates Upregulation of Duox1 and Duox2 and Protects against Lung Injury following Chest Irradiation in Rats
- PMID: 31210428
- PMCID: PMC6582421
- DOI: 10.22074/cellj.2019.6207
Melatonin Attenuates Upregulation of Duox1 and Duox2 and Protects against Lung Injury following Chest Irradiation in Rats
Abstract
Objective: The Lung is one of the most radiosensitive organs of the body. The infiltration of macrophages and lymphocytes into the lung is mediated via the stimulation of T-helper 2 cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-13, which play a key role in the development of fibrosis. It is likely that these cytokines induce chronic oxidative damage and inflammation through the upregulation of Duox1 and Duox2, which can increase the risk of late effects of ionizing radiation (IR) such as fibrosis and carcinogenesis. In the present study, we aimed to evaluate the possible increase of IL-4 and IL-13 levels, as well as their downstream genes such as IL4ra1, IL13ra2, Duox1, and Duox2.
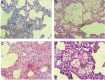
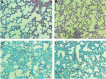
Materials and methods: In this experimental animal study, male rats were divided into 4 groups: i. Control, ii. Melatonintreated, iii. Radiation, and iv. Melatonin (100 mg/kg) plus radiation. Rats were irradiated with 15 Gy 60Co gamma rays and then sacrificed after 67 days. The expressions of IL4ra1, IL13ra2, Duox1, and Duox2, as well as the levels of IL-4 and IL-13, were evaluated. The histopathological changes such as the infiltration of inflammatory cells, edema, and fibrosis were also examined. Moreover, the protective effect of melatonin on these parameters was also determined.
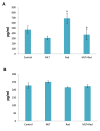
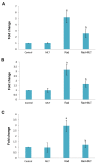
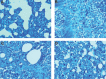
Results: Results showed a 1.5-fold increase in the level of IL-4, a 5-fold increase in the expression of IL4ra1, and a 3-fold increase in the expressions of Duox1 and Duox2. However, results showed no change for IL-13 and no detectable expression of IL13ra2. This was associated with increased infiltration of macrophages, lymphocytes, and mast cells. Melatonin treatment before irradiation completely reversed these changes.
Conclusion: This study has shown the upregulation of IL-4-IL4ra1-Duox2 signaling pathway following lung irradiation. It is possible that melatonin protects against IR-induced lung injury via the downregulation of this pathway and attenuation of inflammatory cells infiltration.
Keywords: Duox1; Duox2; Lung; Melatonin; Radiation.
Copyright© by Royan Institute. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures
References
-
- Yahyapour R, Shabeeb D, Cheki M, Musa AE, Farhood B, Rezaeyan A, et al. Radiation protection and mitigation by natural antioxidants and flavonoids; implications to radiotherapy and radiation disasters. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2018 ahead of print. - PubMed
-
- Mortezaee K, NH Goradel, P Amini, D Shabeeb, A E Musa, M Najafi. NADPH oxidase as a target for modulation of radiation response; implications to carcinogenesis and radiotherapy. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2018 ahead of print. - PubMed
-
- Abratt RP, Morgan GW. Lung toxicity following chest irradiation in patients with lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2002;35(2):103–109. - PubMed
-
- Ghafoori P, Marks LB, Vujaskovic Z, Kelsey CR. Radiation-induced lung injury.Assessment, management, and prevention. Oncology. 2008;22(1):37-47; discussion 52-53.. - PubMed
-
- Tsoutsou PG, Koukourakis MI. Radiation pneumonitis and fibrosis: mechanisms underlying its pathogenesis and implications for future research. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66(5):1281–1293. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
