Methodology and application of Escherichia coli F4 and F18 encoding infection models in post-weaning pigs
- PMID: 31210932
- PMCID: PMC6567477
- DOI: 10.1186/s40104-019-0352-7
Methodology and application of Escherichia coli F4 and F18 encoding infection models in post-weaning pigs
Abstract
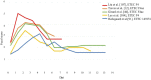
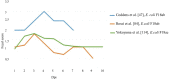
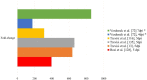
The enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) expressing F4 and F18 fimbriae are the two main pathogens associated with post-weaning diarrhea (PWD) in piglets. The growing global concern regarding antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has encouraged research into the development of nutritional and feeding strategies as well as vaccination protocols in order to counteract the PWD due to ETEC. A valid approach to researching effective strategies is to implement piglet in vivo challenge models with ETEC infection. Thus, the proper application and standardization of ETEC F4 and F18 challenge models represent an urgent priority. The current review provides an overview regarding the current piglet ETEC F4 and F18 challenge models; it highlights the key points for setting the challenge protocols and the most important indicators which should be included in research studies to verify the effectiveness of the ETEC challenge. Based on the current review, it is recommended that the setting of the model correctly assesses the choice and preconditioning of pigs, and the timing and dosage of the ETEC inoculation. Furthermore, the evaluation of the ETEC challenge response should include both clinical parameters (such as the occurrence of diarrhea, rectal temperature and bacterial fecal shedding) and biomarkers for the specific expression of ETEC F4/F18 (such as antibody production, specific F4/F18 immunoglobulins (Igs), ETEC F4/F18 fecal enumeration and analysis of the F4/F18 receptors expression in the intestinal brush borders). On the basis of the review, the piglets' response upon F4 or F18 inoculation differed in terms of the timing and intensity of the diarrhea development, on ETEC fecal shedding and in the piglets' immunological antibody response. This information was considered to be relevant to correctly define the experimental protocol, the data recording and the sample collections. Appropriate challenge settings and evaluation of the response parameters will allow future research studies to comply with the replacement, reduction and refinement (3R) approach, and to be able to evaluate the efficiency of a given feeding, nutritional or vaccination intervention in order to combat ETEC infection.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Challenge; ETEC; Piglet; Post-weaning.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- COMMISSION IMPLEMENTING DECISION of 26.6.2017 concerning, in the framework of Article 35 of Directive 2001/82/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, the marketing authorisations for veterinary medicinal products containing “zinc oxide” to be administered orally to food producing species. 2017. Available from: https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/2017/2017062613....
-
- Roselli M, Pieper R, Rogel-Gaillard C, de Vries H, Bailey M, Smidt H, et al. Immunomodulating effects of probiotics for microbiota modulation, gut health and disease resistance in pigs. Anim Feed Sci Technol. 2017;233:104–119. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2017.07.011. - DOI
-
- Le Floc’h N, Wessels A, Corrent E, Wu G, Bosi P. The relevance of functional amino acids to support the health of growing pigs. Anim Feed Sci Technol. 2018;245:104–116. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2018.09.007. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

