The Alzheimer's Prevention Initiative Generation Program: Study design of two randomized controlled trials for individuals at risk for clinical onset of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 31211217
- PMCID: PMC6562315
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trci.2019.02.005
The Alzheimer's Prevention Initiative Generation Program: Study design of two randomized controlled trials for individuals at risk for clinical onset of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Introduction: Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology, including the accumulation of amyloid beta (Aβ) species and tau pathology, begins decades before the onset of cognitive impairment. This long preclinical period provides an opportunity for clinical trials designed to prevent or delay the onset of cognitive impairment due to AD. Under the umbrella of the Alzheimer's Prevention Initiative Generation Program, therapies targeting Aβ, including CNP520 (umibecestat), a β-site-amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme-1 (BACE-1) inhibitor, and CAD106, an active Aβ immunotherapy, are in clinical development in preclinical AD.
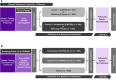
Methods: The Alzheimer's Prevention Initiative Generation Program comprises two pivotal (phase 2/3) studies that assess the efficacy and safety of umibecestat and CAD106 in cognitively unimpaired individuals with high risk for developing symptoms of AD based on their age (60-75 years), APOE4 genotype, and, for heterozygotes (APOE ε2/ε4 or ε3/ε4), elevated brain amyloid. Approximately, 3500 individuals will be enrolled in either Generation Study 1 (randomized to cohort 1 [CAD106 injection or placebo, 5:3] or cohort 2 [oral umibecestat 50 mg or placebo, 3:2]) or Generation Study 2 (randomized to oral umibecestat 50 mg and 15 mg, or placebo [2:1:2]). Participants receive treatment for at least 60 months and up to a maximum of 96 months. Primary outcomes include time to event, with event defined as diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to AD and/or dementia due to AD, and the Alzheimer's Prevention Initiative preclinical composite cognitive test battery. Secondary endpoints include the Clinical Dementia Rating Sum of Boxes, Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status total score, Everyday Cognition Scale, biomarkers, and brain imaging.
Discussion: The Generation Program is designed to assess the efficacy, safety, and biomarker effects of the two treatments in individuals at high risk for AD. It may also provide a plausible test of the amyloid hypothesis and further accelerate the evaluation of AD prevention therapies.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Alzheimer's prevention initiative; BACE-1 inhibitor; CAD106; CNP520; Generation Program; Mild cognitive impairment; Preclinical Alzheimer's disease; Umibecestat.
Figures
References
-
- Sperling R.A., Aisen P.S., Beckett L.A., Bennett D.A., Craft S., Fagan A.M. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer's disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7:280–292. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
