Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma genitalium in Southeastern Region of the Netherlands, 2014-2017
- PMID: 31211669
- PMCID: PMC6590771
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2507.181556
Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma genitalium in Southeastern Region of the Netherlands, 2014-2017
Abstract
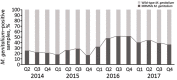
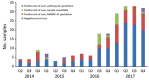
Mycoplasma genitalium infections of the urogenital tract are usually treated with azithromycin; however, for the past several years, rates of azithromycin treatment failure have increased. To document the occurrence and frequency of macrolide resistance-mediating mutations (MRMMs) in M. genitalium infections, we collected 894 M. genitalium-positive samples during April 2014-December 2017 and retrospectively tested them for MRMMs. We designated 67 samples collected within 6 weeks after a positive result as test-of-cure samples; of these, 60 were MRMM positive. Among the remaining 827 samples, the rate of MRMM positivity rose from 22.7% in 2014 and 22.3% in 2015 to 44.4% in 2016 but decreased to 39.7% in 2017. Because of these high rates of MRMMs in M. genitalium infections, we recommend that clinicians perform tests of cure after treatment and that researchers further explore the clinical consequences of this infection.
Keywords: Mycoplasma genitalium; antimicrobial resistance; bacteria; macrolide resistance; molecular diagnostics; sexually transmitted disease; the Netherlands.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma genitalium in Southeastern Region of the Netherlands, 2014-2017.Emerg Infect Dis. 2019 Nov;25(11):2159-2160. doi: 10.3201/eid2511.190912. Epub 2019 Nov 17. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31436528 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma genitalium infections in Cuban patients: an underestimated health problem.BMC Infect Dis. 2018 Nov 29;18(1):601. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3523-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30486786 Free PMC article.
-
High prevalence of the A2058T macrolide resistance-associated mutation in Mycoplasma genitalium strains from the Netherlands.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017 May 1;72(5):1529-1530. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkw584. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28158595 No abstract available.
-
Prevalence of mutations associated with resistance to macrolides and fluoroquinolones in Mycoplasma genitalium: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Nov;20(11):1302-1314. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30154-7. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32622378
-
Mycoplasma genitalium and antimicrobial resistance in Europe: a comprehensive review.Int J STD AIDS. 2020 Mar;31(3):190-197. doi: 10.1177/0956462419890737. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Int J STD AIDS. 2020. PMID: 32000587 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Real-World Effects of Antibiotic Treatment on Acute COPD Exacerbations in Outpatients: A Cohort Study under the PharmLines Initiative.Respiration. 2022;101(6):553-564. doi: 10.1159/000520884. Epub 2022 Jan 3. Respiration. 2022. PMID: 34979502 Free PMC article.
-
Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma genitalium in Southeastern Region of the Netherlands, 2014-2017.Emerg Infect Dis. 2019 Nov;25(11):2159-2160. doi: 10.3201/eid2511.190912. Epub 2019 Nov 17. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31436528 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Evaluating the prevalence and risk factors for macrolide resistance in Mycoplasma genitalium using a newly developed qPCR assay.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 20;15(10):e0240836. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240836. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33079948 Free PMC article.
-
Mycoplasma genitalium: A new superbug.Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2022 Jan-Jun;43(1):1-12. doi: 10.4103/ijstd.ijstd_103_20. Epub 2022 Jun 7. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2022. PMID: 35846530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Mycoplasma genitalium in Primary Care: Prevalence and azithromycin resistance in Santiago de Compostela Health Care Area].Rev Esp Quimioter. 2021 Oct;34(5):496-499. doi: 10.37201/req/052.2021. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2021. PMID: 34286949 Free PMC article. Spanish.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

